Infection due to Mycoplasma hominis after left hip replacement: case report and literature review
- PMID: 30642271
- PMCID: PMC6332536
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-3686-z
Infection due to Mycoplasma hominis after left hip replacement: case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Hip replacement is generally conducted in those with prolonged arthritis pain or hip fractures, and postoperative infection is a serious complication. Mycoplasma hominis, belonging to mycoplasma species, exists mainly in the genitourinary tract. M. hominis infection after total hip replacement was rarely documented in literature.
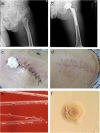
Case presentation: A 59-year-old male was febrile after left total hip replacement. Empiric therapy with cefepime for suspected infection was ineffective. Specimens at the infection site were collected for culture, and pinpoint colonies grew after incubation at 35 °C for 48 h on blood agar plate. They grew to approximately 0.5 mm colonies in diameter after 7-day incubation, and were identified as M. hominis. Sequentially, combination therapy with clindamycin hydrochloride and moxifloxacin was initiated, and the patient defervesced within 3 days and was discharged home.
Conclusions: The study highlighted the potential pathogenicity of M. hominis in postoperative infection. The possibility of this microorganism involvement should be valued if the patients who experienced the hip or joint replacement had inexplicable fever.
Keywords: Hip replacement; Mycoplasma hominis; Postoperative infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The institutional review boards at the Chongqing Shapingba District Chenjiaqiao hospital approved the study protocol.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the editor of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Allen-Daniels MJ, Serrano MG, Pflugner LP, Fettweis JM, Prestosa MA, Koparde VN, Brooks JP, Strauss JF, 3rd, Romero R, Chaiworapongsa T, et al. Identification of a gene in Mycoplasma hominis associated with preterm birth and microbial burden in intraamniotic infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212(6):779. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2015.01.032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

