Therapeutic Inhibition of VEGF Signaling and Associated Nephrotoxicities
- PMID: 30642877
- PMCID: PMC6362621
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2018080853
Therapeutic Inhibition of VEGF Signaling and Associated Nephrotoxicities
Abstract
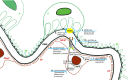
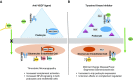
Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA)/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) signaling is a common therapeutic strategy in oncology, with new drugs continuously in development. In this review, we consider the experimental and clinical evidence behind the diverse nephrotoxicities associated with the inhibition of this pathway. We also review the renal effects of VEGF inhibition's mediation of key downstream signaling pathways, specifically MAPK/ERK1/2, endothelial nitric oxide synthase, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Direct VEGFA inhibition via antibody binding or VEGF trap (a soluble decoy receptor) is associated with renal-specific thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA). Reports also indicate that tyrosine kinase inhibition of the VEGF receptors is preferentially associated with glomerulopathies such as minimal change disease and FSGS. Inhibition of the downstream pathway RAF/MAPK/ERK has largely been associated with tubulointerstitial injury. Inhibition of mTOR is most commonly associated with albuminuria and podocyte injury, but has also been linked to renal-specific TMA. In all, we review the experimentally validated mechanisms by which VEGFA-VEGFR2 inhibitors contribute to nephrotoxicity, as well as the wide range of clinical manifestations that have been reported with their use. We also highlight potential avenues for future research to elucidate mechanisms for minimizing nephrotoxicity while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
Keywords: VEGF; hypertension; nitric oxide; proteinuria; signaling.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Ferrara N: VEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 795–803, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Henzel WJ: Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161: 851–858, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Larcher F, Robles AI, Duran H, Murillas R, Quintanilla M, Cano A, et al. : Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor in mouse skin carcinogenesis correlates with malignant progression state and activated H-ras expression levels. Cancer Res 56: 5391–5396, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett N, Phillips HS, et al. : Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 362: 841–844, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Gerber HP, Ferrara N: Pharmacology and pharmacodynamics of bevacizumab as monotherapy or in combination with cytotoxic therapy in preclinical studies. Cancer Res 65: 671–680, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

