A genome-wide association study identifies new loci for factor VII and implicates factor VII in ischemic stroke etiology
- PMID: 30642921
- PMCID: PMC6396174
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-849240
A genome-wide association study identifies new loci for factor VII and implicates factor VII in ischemic stroke etiology
Abstract
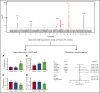
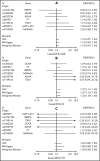
Factor VII (FVII) is an important component of the coagulation cascade. Few genetic loci regulating FVII activity and/or levels have been discovered to date. We conducted a meta-analysis of 9 genome-wide association studies of plasma FVII levels (7 FVII activity and 2 FVII antigen) among 27 495 participants of European and African ancestry. Each study performed ancestry-specific association analyses. Inverse variance weighted meta-analysis was performed within each ancestry group and then combined for a trans-ancestry meta-analysis. Our primary analysis included the 7 studies that measured FVII activity, and a secondary analysis included all 9 studies. We provided functional genomic validation for newly identified significant loci by silencing candidate genes in a human liver cell line (HuH7) using small-interfering RNA and then measuring F7 messenger RNA and FVII protein expression. Lastly, we used meta-analysis results to perform Mendelian randomization analysis to estimate the causal effect of FVII activity on coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke (IS), and venous thromboembolism. We identified 2 novel (REEP3 and JAZF1-AS1) and 6 known loci associated with FVII activity, explaining 19.0% of the phenotypic variance. Adding FVII antigen data to the meta-analysis did not result in the discovery of further loci. Silencing REEP3 in HuH7 cells upregulated FVII, whereas silencing JAZF1 downregulated FVII. Mendelian randomization analyses suggest that FVII activity has a positive causal effect on the risk of IS. Variants at REEP3 and JAZF1 contribute to FVII activity by regulating F7 expression levels. FVII activity appears to contribute to the etiology of IS in the general population.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: W.M. reports grants and personal fees from AMGEN, BASF, Sanofi, Siemens Diagnostics, Aegerion Pharmaceuticals, Astrazeneca, Danone Research, Numares, Pfizer, and Hoffmann LaRoche; personal fees from MSD and Alexion; grants from Abbott Diagnostics, all outside of the submitted work; and is employed by Synlab Holding Deutschland GmbH. B.M.P. serves on the Data Safety Monitoring Board of a clinical trial funded by Zoll LifeCor and on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. N.M.D. reports a grant for research unrelated to this work from the Global Research Awards for Nicotine Dependence (GRAND), an independent grant-making body funded by Pfizer. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lapecorella M, Mariani G; International Registry on Congenital Factor VII Deficiency. Factor VII deficiency: defining the clinical picture and optimizing therapeutic options. Haemophilia. 2008;14(6):1170-1175. - PubMed
-
- Smith A, Patterson C, Yarnell J, Rumley A, Ben-Shlomo Y, Lowe G. Which hemostatic markers add to the predictive value of conventional risk factors for coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke? The Caerphilly Study. Circulation. 2005;112(20):3080-3087. - PubMed
-
- Tsai AW, Cushman M, Rosamond WD, et al. . Coagulation factors, inflammation markers, and venous thromboembolism: the longitudinal investigation of thromboembolism etiology (LITE). Am J Med. 2002;113(8):636-642. - PubMed
-
- Folsom AR. Hemostatic risk factors for atherothrombotic disease: an epidemiologic view. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86(1):366-373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004729/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102419/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL103612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 NS100605/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5RC2HL102419/RA/ARRA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_00011/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004424/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300025C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300027C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900041C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300028C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS105150/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/9/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300029C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134894/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

