Active control of arousal by a locus coeruleus GABAergic circuit
- PMID: 30643295
- PMCID: PMC6385895
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-018-0305-z
Active control of arousal by a locus coeruleus GABAergic circuit
Abstract
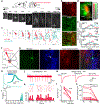
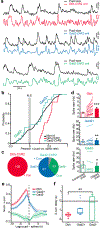
Arousal responses linked to locus coeruleus noradrenergic (LC-NA) activity affect cognition. However, the mechanisms that control modes of LC-NA activity remain unknown. Here, we reveal a local population of GABAergic neurons (LC-GABA) capable of modulating LC-NA activity and arousal. Retrograde tracing shows that inputs to LC-GABA and LC-NA neurons arise from similar regions, though a few regions provide differential inputs to one subtype over the other. Recordings in the locus coeruleus demonstrate two modes of LC-GABA responses whereby spiking is either correlated or broadly anticorrelated with LC-NA responses, reflecting anatomically similar and functionally coincident inputs, or differential and non-coincident inputs, to LC-NA and LC-GABA neurons. Coincident inputs control the gain of LC-NA-mediated arousal responses, whereas non-coincident inputs, such as from the prefrontal cortex to the locus coeruleus, alter global arousal levels. These findings demonstrate distinct modes by which an inhibitory locus coeruleus circuit regulates arousal in the brain.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

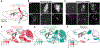
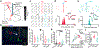


References
-
- Aston-Jones G & Cohen JD An integrative theory of locus coeruleus-norepinephrine function: adaptive gain and optimal performance. Annual review of neuroscience 28, 403–450 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Sara SJ The locus coeruleus and noradrenergic modulation of cognition. Nature reviews. Neuroscience 10, 211–223 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Sara SJ & Bouret S Orienting and reorienting: the locus coeruleus mediates cognition through arousal. Neuron 76, 130–141 (2012). - PubMed
Methods-only References:
-
- Paxinos G & Franklin KB J. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (Academic Press, San Diego, California, 2001).
-
- Lein ES, et al. Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 445, 168–176 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

