Safety and efficacy of twice daily administration of KPI-121 1% for ocular inflammation and pain following cataract surgery
- PMID: 30643381
- PMCID: PMC6311334
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S185800
Safety and efficacy of twice daily administration of KPI-121 1% for ocular inflammation and pain following cataract surgery
Abstract
Purpose: KPI-121 is a nanoparticle suspension of loteprednol etabonate with improved ocular pharmacokinetics compared with marketed formulations. The efficacy and safety of KPI-121 1% ophthalmic suspension (INVELTYS™) dosed twice daily (BID) were evaluated in participants who had undergone cataract surgery.
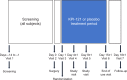
Materials and methods: In two multicenter, randomized, double-masked, parallel-group, vehicle-controlled clinical trials, 386 participants with ≥ grade 2 anterior chamber cells (≥6 cells) on the day following routine cataract surgery were treated with KPI-121 1% and 325 participants were treated with placebo (vehicle); each group was dosed BID for 2 weeks. Primary efficacy endpoints were complete resolution of ocular inflammation by slit-lamp biomicroscopy and complete resolution of subject-rated ocular pain at Days 8 and 15 with no rescue medication before Day 15. Safety assessments included adverse events (AEs), visual acuity, intraocular pressure measurements, and evaluation of ocular AEs by slit-lamp biomicroscopy and dilated ophthalmoscopy.
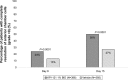
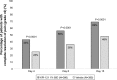
Results: Both trials achieved statistical significance favoring KPI-121 1% BID for both primary efficacy endpoints. Combined data analysis showed that significantly more participants treated with KPI-121 vs vehicle achieved complete resolution of anterior chamber cells at Days 8 and 15 (P≤0.0001) and complete clearing of ocular pain at Days 4, 8, and 15 (P<0.0001). AEs were reported more frequently with vehicle than KPI-121.
Conclusion: KPI-121 1% ophthalmic suspension was effective in resolving postoperative ocular inflammation and pain when dosed BID for 2 weeks in patients following cataract surgery. KPI-121 was found to be safe and well tolerated in both trials.
Keywords: loteprednol etabonate; mucus penetrating particles; nanoparticle; pain; postoperative ocular inflammation.
Figures
References
-
- American Academy of Ophthalmology Cataract in the adult eye: preferred practice patterns. 2016. [Accessed May 28, 2018]. Available from: https://www.aao.org/preferred-practice-pattern/cataract-in-adult-eye-ppp....
-
- El-Harazi SM, Feldman RM. Control of intra-ocular inflammation associated with cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2001;12(1):4–8. - PubMed
-
- Shoss BL, Tsai LM. Postoperative care in cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2013;24(1):66–73. - PubMed
-
- Leopold IH. Update on antibiotics in ocular infections. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985;100(1):134–140. - PubMed
-
- INVELTYS™ (loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension 1%) [package insert] Waltham, MA: Kala Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

