The efficacy of pregabalin for the management of acute and chronic postoperative pain in thoracotomy: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized-controlled trials
- PMID: 30643448
- PMCID: PMC6312398
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S183411
The efficacy of pregabalin for the management of acute and chronic postoperative pain in thoracotomy: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized-controlled trials
Abstract
Purpose: Pregabalin is commonly used as an analgesic for neuropathic pain. But pregabalin as an adjunct to a multimodal analgesic regimen - although standard clinical protocol in some settings - has remained controversial. This meta-analysis was conducted to identify the efficacy of pregabalin for management of postoperative pain in thoracotomy.
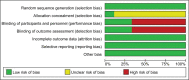
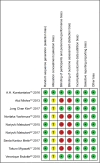
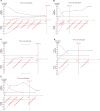
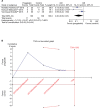
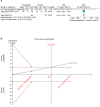
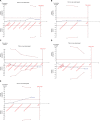
Materials and methods: Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane, Web of Science, Springer, and Clinical Trial Register database were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of pregabalin in preventing postoperative pain in thoracotomy. Review Manager 5.3 and STATA 12.0 were selected to conduct the meta-analysis. Trial sequential analysis was used to control random errors and calculate the required information size.
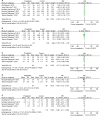
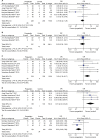
Results: Nine RCTs with 684 patients were included in our meta-analysis. Outcomes favoring pregabalin included less pain on a 0-10 scale on 1 day [mean difference (MD): -0.87; 95% CI: -1.55 to -0.19; P=0.01], 3 days (MD: -1.55; 95% CI: -1.93 to -1.18; P<0.00001), 1 month (MD: -1.58; 95% CI: -2.75 to -0.42; P=0.008), 3 months (MD: -1.69; 95% CI: -2.71 to -0.66; P=0.001) postoperatively, and less incidence of neuropathic pain (OR: 0.20; 95% CI: 0.05-0.91; P=0.04), less mean morphine consumption (MD: -5.03; 95% CI: -8.06 to -1.99; P=0.001), but more dizziness (OR: 3.33; 95% CI: 1.36-8.17; P=0.009), more drowsiness (OR: 8.61; 95% CI: 2.23-33.20; P=0.002), and less constipation (OR: 0.23; 95% CI: 0.09-0.59; P=0.002). There was no statistical differences in pain score on 7 days (MD:-0.77; 95% CI: -2.38 to 0.84; P=0.35), nausea (OR: 0.73; 95% CI: 0.42-1.26; P=0.26), and vomiting (OR: 0.83; 95% CI: 0.36-1.90; P=0.65).
Conclusion: Pregabalin can prevent postoperative pain in thoracotomy and decrease incidence of neuropathic pain and morphine consumption. Pregabalin may be a valuable asset in management of acute and persistent postoperative pain in thoracotomy.
Keywords: meta-analysis; neuropathic pain; postoperative pain; pregabalin; thoracotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Joshi GP, Bonnet F, Shah R, et al. A systematic review of randomized trials evaluating regional techniques for postthoracotomy analgesia. Anesth Analg. 2008;107(3):1026–1040. - PubMed
-
- Kehlet H, Dahl JB. The value of “multimodal” or “balanced analgesia” in postoperative pain treatment. Anesth Analg. 1993;77(5):1048–1056. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

