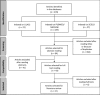
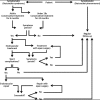
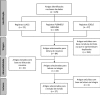
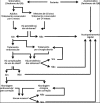
Diagnosis and treatment of the Nutcracker syndrome: a review of the last 10 years
- PMID: 30643508
- PMCID: PMC6326141
- DOI: 10.1590/1677-5449.012417
Diagnosis and treatment of the Nutcracker syndrome: a review of the last 10 years
Abstract
The nutcracker syndrome is characterized by a group of clinical manifestations caused by compression of the Left Renal Vein. The main symptoms are: macro and micro hematuria, proteinuria, and flank pain. Diagnosis is usually made after excluding other causes, because there are no clinical criteria for diagnosis. Confirmation is by Doppler ultrasonography or computed tomography. Treatment can vary, depending on patient characteristics and the severity of the symptoms, while conservative treatment, open surgery, and endovascular surgery may be employed. Currently, open surgery is still the first-line treatment, but some less invasive approaches are gaining acceptance.
Resumo: A síndrome de quebra-nozes é caracterizada por um grupo de manifestações clínicas que ocorrem por conta da compressão da veia renal esquerda. Seus principais sintomas são macro e micro-hematúria, proteinúria e dor no flanco. O diagnóstico é geralmente realizado após a exclusão de outras causas mais comuns, por conta da ausência de critérios clínicos para diagnóstico. Sua confirmação é feita por exames de imagem, com uso da ultrassonografia Doppler e tomografia computadorizada. O tratamento pode variar com as características do paciente e com a gravidade dos sintomas, e inclui o tratamento conservador, a cirurgia aberta e a cirurgia endovascular. Atualmente, a cirurgia aberta continua sendo a linha de frente, mas abordagens menos invasivas vêm ganhando cada vez mais espaço.
Keywords: hematuria; nephrectomy; renal nutcracker syndrome; stents.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: No conflicts of interest declared concerning the publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Calado R, Braz M, Lobo L, Simão C. Síndrome de Nutcracker: hematúria sem diagnóstico. Acta Med Port. 2011;24(Suppl 3):695–698. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources