Laparoscopic treatment of celiac axis compression by the median arcuate ligament and endovascular repair of a pancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysm: case report
- PMID: 30643513
- PMCID: PMC6326135
- DOI: 10.1590/1677-5449.000118
Laparoscopic treatment of celiac axis compression by the median arcuate ligament and endovascular repair of a pancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysm: case report
Abstract
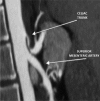
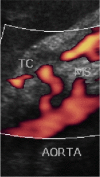
Compression of the celiac axis by the median arcuate ligament of the diaphragm can cause nonspecific symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting, and weight loss. There is a known association between stenosis or occlusion of the celiac trunk and aneurysms of the pancreaticoduodenal artery. Treatment strategies for patients who have this association should be selected on a case-by-case basis. We describe the case of a patient with pancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysm associated with compression of the celiac trunk by the arcuate ligament, which were managed with endovascular and laparoscopic techniques, respectively.
Resumo: A compressão do tronco celíaco pelo ligamento arqueado mediano do diafragma pode causar sintomas inespecíficos como dor abdominal, vômitos e emagrecimento. Existe uma associação comprovada entre estenoses ou oclusões do tronco celíaco e aneurismas da artéria pancreatoduodenal. Nas situações em que essa associação ocorre, a estratégia de tratamento deve ser individualizada. Relatamos o caso de uma paciente com aneurisma de artéria pancreatoduodenal associado à compressão do tronco celíaco pelo ligamento arqueado, manejados, respectivamente, por técnicas endovasculares e laparoscópicas.
Keywords: celiac plexus compression; median arcuate ligament syndrome; pancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysm.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: No conflicts of interest declared concerning the publication of this article.
Figures






References
-
- Thevenet A, Domergue J, Joyeux A. Surgical treatment of stenoses of the celiac trunk caused by the arcuate ligament of the diaphragm. Long-term results. Chirurgie. 1985;111(10):851–856. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
