Terbutaline alleviates the lung injury in the neonatal rats exposed to endotoxin: Potential roles of epithelial sodium channels
- PMID: 30644180
- PMCID: PMC6618278
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.24242
Terbutaline alleviates the lung injury in the neonatal rats exposed to endotoxin: Potential roles of epithelial sodium channels
Abstract
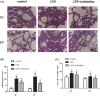
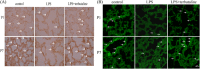
Intrauterine inflammation generates inflammatory mediators that damage the developing bronchoalveolar epithelium, resulting in neonatal lung injury. Lung fluid transport disorders are the main reasons for the development of pulmonary edema, an important pathology of lung injury. Previous studies suggested that epithelial sodium channels (ENaCs) play an important role in lung fluid transport. Here, we investigated whether changes in the expression of ENaCs were observed when neonatal rat lung injury was induced by maternal exposure to endotoxin. We also examined the therapeutic effect of terbutaline nebulizer inhalation on this injury. The results showed that maternal exposure to endotoxin increased the levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, suppressed α-, β-, γ-ENaC in the neonatal rat lung, and resulted in the formation of pulmonary edema on postnatal days 1 and 7. Terbutaline up-regulated the expression of β- and γ-ENaC in the distal lung after 7 days of treatment. The potential signal molecules cAMP, PKA, and CREB expressions were increased after terbutaline treatment. In summary, maternal exposure to endotoxin decreased the expression of ENaCs in neonatal rats which, in turn, may exacerbate pulmonary edema. Inhalation of the β2-adrenergic receptor agonist terbutaline improved lung liquid clearance. By increasing the expression of sodium ion channels, the effective removal of alveolar fluid provides a new way for the prevention and treatment of neonatal lung injury.
Keywords: endotoxin; epithelial sodium channels; lung injury; neonatal rat; terbutaline.
© 2019 The Authors. Pediatric Pulmonology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


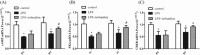
Similar articles
-
Ursodeoxycholic acid stimulates alveolar fluid clearance in LPS-induced pulmonary edema via ALX/cAMP/PI3K pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Nov;234(11):20057-20065. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28602. Epub 2019 Apr 10. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30972764
-
Adenosine A2B receptor activation stimulates alveolar fluid clearance through alveolar epithelial sodium channel via cAMP pathway in endotoxin-induced lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Apr 1;318(4):L787-L800. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00195.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32129084
-
Long-term terbutaline exposure stimulates alpha1-Na+-K+-ATPase expression at posttranscriptional level in rat fetal distal lung epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 Jan;298(1):L96-L104. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00158.2009. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19880505
-
Treatment of pulmonary edema by ENaC activators/stimulators.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;6(1):13-27. doi: 10.2174/1874467211306010003. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23547931 Review.
-
Alveolar epithelial fluid transport in acute lung injury: new insights.Eur Respir J. 2002 Nov;20(5):1299-313. doi: 10.1183/09031936.02.00401602. Eur Respir J. 2002. PMID: 12449188 Review.
Cited by
-
Protectin conjugates in tissue regeneration 1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting ferroptosis.J Transl Med. 2023 Apr 30;21(1):293. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04111-9. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37121999 Free PMC article.
-
Erythrocyte membrane affinity chromatography, solid-phase extraction and UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS to screen active ingredients of Buyang Huanwu decoction.RSC Adv. 2019 Sep 17;9(50):29217-29224. doi: 10.1039/c9ra03447a. eCollection 2019 Sep 13. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35528420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang H, Gao X, Liu C, et al. Morbidity and mortality of neonatal respiratory failure in China: surfactant treatment in very immature infants. Pediatrics. 2012;129:e731–e740. - PubMed
-
- Altman M, Vanpee M, Cnattingius S, Norman M. Risk factors for acute respiratory morbidity in moderately preterm infants. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2013;27:172–181. - PubMed
-
- Bersani I, Thomas W, Speer CP. Chorioamnionitis‐the good or the evil for neonatal outcome? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25:12–16. - PubMed
-
- Westover AJ, Moss TJ. Effects of intrauterine infection or inflammation on fetal lung development. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;39:824–830. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

