GABA Transaminase Deficiency With Survival Into Adulthood
- PMID: 30644311
- PMCID: PMC7292229
- DOI: 10.1177/0883073818823359
GABA Transaminase Deficiency With Survival Into Adulthood
Abstract
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA)-transaminase deficiency is an ultra-rare disorder of GABA metabolism that was described for decades as an early-onset epileptic encephalopathy plus movement disorder and hypersomnolence with mortality in early childhood. We report 2 affected siblings in adolescence and adulthood, both with profound developmental impairment, intractable epilepsy, movement disorder, and behavioral fluctuations. This considerably expands the phenotype and longevity of this inherited neurotransmitter disease.
Keywords: ABAT gene; GABA metabolism; GABA-T deficiency; GABA-transaminase deficiency; India.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests:
Anaita U. Hegde reports no disclosures or conflicts of interest
Purva K. Karnavat reports no disclosures or conflicts of interest
R. Vyas reports no disclosures or conflicts of interest
Melissa L. DiBacco reports no disclosures or conflicts of interest
P. Ellen Grant reports no disclosures or conflicts of interest
Phillip L. Pearl reports no disclosures or conflicts of interest
Figures

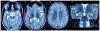
Similar articles
-
Personalized medicine approach confirms a milder case of ABAT deficiency.Mol Brain. 2016 Dec 1;9(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13041-016-0273-8. Mol Brain. 2016. PMID: 27903293 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotyping GABA transaminase deficiency: a case description and literature review.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2016 Sep;39(5):743-747. doi: 10.1007/s10545-016-9951-z. Epub 2016 Jul 4. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2016. PMID: 27376954
-
Clinical aspects of the disorders of GABA metabolism in children.Curr Opin Neurol. 2004 Apr;17(2):107-13. doi: 10.1097/00019052-200404000-00005. Curr Opin Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15021235 Review.
-
Identification of a familial mutation associated with GABA-transaminase deficiency disease.Neurobiol Dis. 1998 Aug;5(2):89-96. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.1998.0184. Neurobiol Dis. 1998. PMID: 9746906
-
Phenotype of GABA-transaminase deficiency.Neurology. 2017 May 16;88(20):1919-1924. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003936. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Neurology. 2017. PMID: 28411234 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational Exploration of the Effects of Mutations on GABA Aminotransferase in GABA Aminotransferase Deficiency.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 30;24(13):10933. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310933. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446113 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic pathways and genes involved in treatable and non-treatable metabolic epilepsies. A comprehensive review and metabolic pathway analysis.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Mar 14;40(3):152. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01562-5. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40085371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotransmission-related gene expression in the frontal pole is altered in subjects with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Apr 8;13(1):118. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02418-1. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37031222 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling of GABA Metabolism to Mitochondrial Glucose Phosphorylation.Neurochem Res. 2022 Feb;47(2):470-480. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03463-2. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 34623563
-
Epilepsy in inherited neurotransmitter disorders: Spotlights on pathophysiology and clinical management.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Jan;36(1):29-43. doi: 10.1007/s11011-020-00635-x. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 33095372 Review.
References
-
- Jaeken J, Casaer P, de Cock P, et al. Gamma-aminobutyric acid-transaminase deficiency: a newly recognized inborn error of neurotransmitter metabolism. Neuropediatrics 1984; 15(3): 165–169. - PubMed
-
- Nagappa M, Bindu PS, Chiplunkar S, et al. Hypersomnolence-hyperkinetic movement disorder in a child with compound heterozygous mutation in 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT) gene. Brain Dev 2016;39:161–165. - PubMed
-
- Jakobs C, Jaeken J Gibson KM. Inherited disorders of GABA metabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis 1993; 16(4): 704–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

