CD33 recruitment inhibits IgE-mediated anaphylaxis and desensitizes mast cells to allergen
- PMID: 30645205
- PMCID: PMC6391081
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI125456
CD33 recruitment inhibits IgE-mediated anaphylaxis and desensitizes mast cells to allergen
Abstract
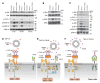
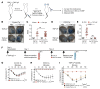
Allergen immunotherapy for patients with allergies begins with weekly escalating doses of allergen under medical supervision to monitor and treat IgE mast cell-mediated anaphylaxis. There is currently no treatment to safely desensitize mast cells to enable robust allergen immunotherapy with therapeutic levels of allergen. Here, we demonstrated that liposomal nanoparticles bearing an allergen and a high-affinity glycan ligand of the inhibitory receptor CD33 profoundly suppressed IgE-mediated activation of mast cells, prevented anaphylaxis in Tg mice with mast cells expressing human CD33, and desensitized mice to subsequent allergen challenge for several days. We showed that high levels of CD33 were consistently expressed on human skin mast cells and that the antigenic liposomes with CD33 ligand prevented IgE-mediated bronchoconstriction in slices of human lung. The results demonstrated the potential of exploiting CD33 to desensitize mast cells to provide a therapeutic window for administering allergen immunotherapy without triggering anaphylaxis.
Keywords: Glycobiology; Immunology; Mast cells; Nanotechnology; Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Comment in
-
Recruiting CD33 on mast cells to inhibit IgE-mediated mast cell-dependent anaphylaxis.J Clin Invest. 2019 Mar 1;129(3):955-957. doi: 10.1172/JCI127100. Epub 2019 Feb 18. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30776022 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

