The effects of the flipped classroom in teaching evidence based nursing: A quasi-experimental study
- PMID: 30645609
- PMCID: PMC6333329
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210606
The effects of the flipped classroom in teaching evidence based nursing: A quasi-experimental study
Abstract
Background: Evidence-based nursing (EBN) has been an important training mechanism for improving the quality of clinical care. At present, the pedagogy focuses on the application of e-learning and team-based learning to enhance learners' engagement and learning effectiveness.
Objectives: This study applied the flipped classroom approach to conduct evidence-based nursing (EBN) teaching. The aim of this study is to elevate the learning effectiveness of the flipped classroom group to the traditional teaching group in terms of knowledge and self-efficacy in practice.
Design: A pretest-posttest nonequivalent control group with a quasi-experimental quantitative design.
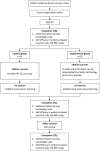
Methods: The study recruited 151 nurses, of whom 75 were in the control group and 76 were in the experimental group. During the EBN course, the control group received training via traditional pedagogy while the experimental group engaged the flipped classroom approach. The learning effectiveness of EBN knowledge and self-efficacy in practice were evaluated across the three time points: pre-course, post-course, and one month after the course.
Results: In both group the scores of the EBN knowledge and self-efficacy in practice improved after training. The scores of the experimental group increased significantly than in the control group. However, the scores declined in both groups one month after the course. Even so, the experimental group's score of self-efficacy in practice was still higher than that of the control group.
Conclusion: The implementation of the flipped classroom approach and team-based learning effectively enhanced the learners EBN knowledge accumulation and self-efficacy in practice. The research results can be used as an important reference for improving clinical nursing teaching quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Similar articles
-
Comparing the effects of traditional lecture and flipped classroom on nursing students' critical thinking disposition: A quasi-experimental study.Nurse Educ Today. 2018 Dec;71:151-156. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2018.09.027. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Nurse Educ Today. 2018. PMID: 30286373
-
Paradoxical effect of flipped classroom on nursing students' learning ability and satisfaction in a fundamental of nursing clinical course: A quasi-experimental study.J Prof Nurs. 2025 Mar-Apr;57:112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.profnurs.2025.01.011. Epub 2025 Jan 30. J Prof Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40074373
-
Self-directed learning readiness and learning achievements of a flipped classroom model approach in research methods class: A quasi-experimental study.Nurse Educ Pract. 2024 May;77:103968. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2024.103968. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Nurse Educ Pract. 2024. PMID: 38640708
-
An Integrative Review of Flipped Classroom Teaching Models in Nursing Education.J Prof Nurs. 2017 Mar-Apr;33(2):133-144. doi: 10.1016/j.profnurs.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Jul 22. J Prof Nurs. 2017. PMID: 28363388 Review.
-
The effectiveness of a flipped classroom on the development of Chinese nursing students' skill competence: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Nurse Educ Today. 2019 Sep;80:67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2019.06.005. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Nurse Educ Today. 2019. PMID: 31279251
Cited by
-
A Survey of College Students on the Preference for Online Teaching Videos of Variable Durations in Online Flipped Classroom.Front Public Health. 2022 Mar 9;10:838106. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.838106. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35356026 Free PMC article.
-
Experiences of nursing students under the unprecedented abrupt online learning format forced by the national curfew due to COVID-19: A qualitative research study.Nurse Educ Today. 2021 May;100:104829. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2021.104829. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Nurse Educ Today. 2021. PMID: 33740705 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Flipped Classroom through Near Peer Education (FC through NPE) on patient safety knowledge retention in nursing and midwifery students: a solomon four-group design.BMC Med Educ. 2022 Feb 19;22(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03144-w. BMC Med Educ. 2022. PMID: 35183160 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of evidence-based nursing practices training programme on the competency of nurses caring for mechanically ventilated patients: a randomised controlled trial.BMC Nurs. 2024 Apr 2;23(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-01869-1. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38566049 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the online flipped classroom on self-directed learning readiness and metacognitive awareness in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic.BMC Nurs. 2022 Jan 19;21(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12912-022-00804-6. BMC Nurs. 2022. PMID: 35042484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McConnell ES, Lekan D, Bunn M, Egerton E, Corazzini KN, Hendrix CD, et al. Teaching evidence-based nursing practice in geriatric care settings: the geriatric nursing innovations through education institute. Journal of Gerontological Nursing. 2009; 35(4): 26–33; quiz 34–25. - PubMed
-
- <j/>Melnyk BM, Fineout-Overholt E. Evidence-based practice in nursing & healthcare: A guide to best practice. 2nd eds Philadelphia, WK: Lippincott; 2011.
-
- Melnyk B., Fineout-Overholt E., Stillwell S., Williamson K. (2010). Evidence-based Practice: Step by Step. The Seven Steps of Evidence-based Practice. American Journal Of Nursing, 110(1), 51–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources