An Interferon-Driven Oxysterol-Based Defense against Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
- PMID: 30645975
- PMCID: PMC6336114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.12.001
An Interferon-Driven Oxysterol-Based Defense against Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
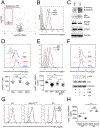
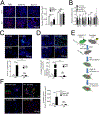
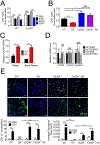
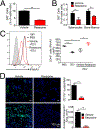
Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (TEV) "educate" healthy cells to promote metastases. We found that melanoma TEV downregulated type I interferon (IFN) receptor and expression of IFN-inducible cholesterol 25-hydroxylase (CH25H). CH25H produces 25-hydroxycholesterol, which inhibited TEV uptake. Low CH25H levels in leukocytes from melanoma patients correlated with poor prognosis. Mice incapable of downregulating the IFN receptor and Ch25h were resistant to TEV uptake, TEV-induced pre-metastatic niche, and melanoma lung metastases; however, ablation of Ch25h reversed these phenotypes. An anti-hypertensive drug, reserpine, suppressed TEV uptake and disrupted TEV-induced formation of the pre-metastatic niche and melanoma lung metastases. These results suggest the importance of CH25H in defense against education of normal cells by TEV and argue for the use of reserpine in adjuvant melanoma therapy.
Keywords: 25-hydroxycholesterol; IFNAR1; adjuvant therapy; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; interferon; melanoma; metastasis; pre-metastatic niche; reserpine.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Tumor Extracellular Vesicles Impede Interferon Alert Responses.Cancer Cell. 2019 Jan 14;35(1):3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.12.006. Cancer Cell. 2019. PMID: 30645974
References
-
- Anggakusuma, Romero-Brey I, Berger C, Colpitts CC, Boldanova T, Engelmann M, Todt D, Perin PM, Behrendt P, Vondran FW, et al. (2015). Interferon-inducible cholesterol-25-hydroxylase restricts hepatitis C virus replication through blockage of membranous web formation. Hepatology 62, 702–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

