A single metabolite production by Escherichia coli BW25113 and its pflA.cra mutant cultivated under microaerobic conditions using glycerol or glucose as a carbon source
- PMID: 30647652
- PMCID: PMC6296642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2017.01.004
A single metabolite production by Escherichia coli BW25113 and its pflA.cra mutant cultivated under microaerobic conditions using glycerol or glucose as a carbon source
Abstract
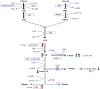
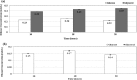
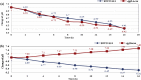
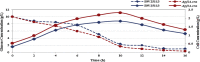
Abundant, low prices and a highly reduced nature make glycerol to be an ideal feedstock for the production of reduced biochemicals and biofuels. Escherichia coli has been paid much attention as the platform of microbial cell factories due to its high growth rate (giving higher metabolite production rate) and the capability of utilizing a wide range of carbon sources. However, one of the drawbacks of using E. coli as a platform is its mixed metabolite formation under anaerobic conditions. In the present study, it was shown that ethanol could be exclusively produced from glycerol by the wild type E. coli, while d-lactic acid could be exclusively produced from glucose by pflA.cra mutant, where the glucose uptake rate could be increased by this mutant as compared to the wild type strain. It was also shown that the growth rate is significantly reduced in pflA.cra mutant for the case of using glycerol as a carbon source due to redox imbalance. The metabolic regulation mechanisms behind the fermentation characteristic were clarified to some extent.
Keywords: ATP, adenosine triphosphate; AcCoA, acetyl-coenzyme A; Biofuel; DCW, dry cell weight; DHA, dihydroxyacetone; Escherichia coli; Ethanol production; GAPDH, -glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; Glucose; Glycerol; KH2PO4, potassium dihydrogen phosphate; KOH, potassium hydroxide; LB, Luria Bertani; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; M9, type of minimal media; MgSO4, magnesium sulfate; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADH, reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; Na2HPO4, sodium phosphate; NaCl, sodium chloride; NaOH, sodium hydroxide; OAA, oxaloacetic Acid; OD, optical density; PEP, phosphoenol pyruvate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvic acid; PTS, phospho-transferase system; PYR, pyruvate; Pfl, pyruvate formatelyase; TCA, tri-carboxylic acid; UV, ultra violet; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; cAMP-Crp, cAMP receptor protein; pflA.cra mutant.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
