Antifibrotic Effect of Marine Ovothiol in an In Vivo Model of Liver Fibrosis
- PMID: 30647809
- PMCID: PMC6311726
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/5045734
Antifibrotic Effect of Marine Ovothiol in an In Vivo Model of Liver Fibrosis
Abstract
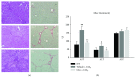
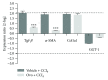
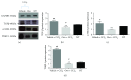
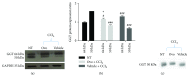
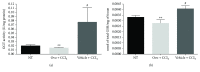
Liver fibrosis is a complex process caused by chronic hepatic injury, which leads to an excessive increase in extracellular matrix protein accumulation and fibrogenesis. Several natural products, including sulfur-containing compounds, have been investigated for their antifibrotic effects; however, the molecular mechanisms underpinning their action are partially still obscure. In this study, we have investigated for the first time the effect of ovothiol A, π-methyl-5-thiohistidine, isolated from sea urchin eggs on an in vivo murine model of liver fibrosis. Mice were intraperitoneally injected with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) to induce liver fibrosis and treated with ovothiol A at the dose of 50 mg/kg 3 times a week for 2 months. Treatment with ovothiol A caused a significant reduction of collagen fibers as observed by histopathological changes and serum parameters compared to mice treated with control solution. This antifibrotic effect was associated to the decrease of fibrogenic markers involved in liver fibrosis progression, such as the transforming growth factor (TGF-β), the α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), and the tissue metalloproteinases inhibitor (TIMP-1). Finally, we provided evidence that the attenuation of liver fibrosis by ovothiol A treatment can be regulated by the expression and activity of the membrane-bound γ-glutamyl-transpeptidase (GGT), which is a key player in maintaining intracellular redox homoeostasis. Overall, these findings indicate that ovothiol A has significant antifibrotic properties and can be considered as a new marine drug or dietary supplement in potential therapeutic strategies for the treatment of liver fibrosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antifibrotic action of telmisartan in experimental carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in Wistar rats.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016;57(4):1261-1272. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016. PMID: 28174792
-
Mistletoe alkaloid fractions alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis through inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation via TGF-β/Smad interference.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Dec 2;158 Pt A:230-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.10.028. Epub 2014 Oct 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25456431
-
Diethylcarbamazine attenuates the expression of pro-fibrogenic markers and hepatic stellate cells activation in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis.Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Apr;26(2):599-609. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0329-0. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28409388
-
Natural Sulfur-Containing Compounds: An Alternative Therapeutic Strategy against Liver Fibrosis.Cells. 2019 Oct 30;8(11):0. doi: 10.3390/cells8111356. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31671675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibrosis of liver, pancreas and intestine: common mechanisms and clear targets?Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2000 Oct-Dec;63(4):366-70. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2000. PMID: 11233519 Review.
Cited by
-
The first genetic engineered system for ovothiol biosynthesis in diatoms reveals a mitochondrial localization for the sulfoxide synthase OvoA.Open Biol. 2023 Feb;13(2):220309. doi: 10.1098/rsob.220309. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Open Biol. 2023. PMID: 36722300 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of HIF-1α Attenuates Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 1;19(11):6775. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116775. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35682354 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Light Response of Skeletonema marinoi: Involvement of Ovothiol.Mar Drugs. 2020 Sep 20;18(9):477. doi: 10.3390/md18090477. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32962291 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Thiols: A Potential Supporting Strategy against Oxidative Stress in Heart Failure and Muscular Damage during Sports Activity.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Dec 16;17(24):9424. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17249424. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33339141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Marine Natural Products on Liver Diseases.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jun 21;22(7):288. doi: 10.3390/md22070288. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39057397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

