Comparative study on amount of nutraceuticals in by-products from solvent and cold pressing methods of rice bran oil processing
- PMID: 30648596
- PMCID: PMC9298647
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.06.006
Comparative study on amount of nutraceuticals in by-products from solvent and cold pressing methods of rice bran oil processing
Abstract
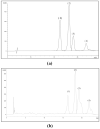
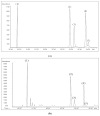
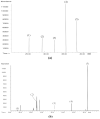
Rice bran oil (RBO) has become a popular oil globally. However, the RBO extraction process leaves various residue products, which contain bioactive substances of varying potency which could be significant sources of functional ingredients for both food production and pharmaceutical manufacture. The objective of our study was to compare the bioactive substances in various by-products derived from the two rice bran oil processing methods; solvent extraction and cold pressing. The residues from solvent extraction processing contained up to 97.37 mg/100 g of γ-aminobutyric acid in defatted rice bran, and the rice acid oil contained high levels of vitamin E (tocopherols, tocotrienols), up to 120.59 mg/100 g, as well as γ-oryzanol (3829.65 mg/100 g), phytosterol (599.40 mg/100 g), and policosanol compounds (332.79 mg/100 g). All of these values are higher than in the residues derived from cold pressing. Importantly, high amounts of total nutraceuticals (8.3 kg/100 kg) were found in residues from both processing methods, indicating the commercial potential of these residues as a source of functional ingredients for food production, as dietary supplements, and in pharmaceutical manufacture.
Keywords: By-products; Cold pressing process; Nutraceutical; Refining process; Rice bran oil.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Thai Rice Exporters Association. Thai rice production, consumption, and stocks. 2016. [Accessed 24 April 2017]. http://www.thairiceexporters.or.th/production.htm .
-
- Prasad MN, Sanjay K, Khatokar MS, Vismaya M, Swamy SN. Health benefits of rice Bran - a review. J Nutr Food Sci. 2011;01:1–7. doi: 10.4172/2155-9600.1000108. - DOI
-
- Pestana VR, Zambiazi RC, Mendonça CRB, Bruscatto MH, Ramis-Ramos G. The influence of industrial processing on the physico-chemical characteristics and lipid and antioxidant contents of rice bran. Grasas Aceites. 2009;60:184–93. doi: 10.3989/gya.075108. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
