Brainstem spreading depolarization and cortical dynamics during fatal seizures in Cacna1a S218L mice
- PMID: 30649209
- PMCID: PMC6351775
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awy325
Brainstem spreading depolarization and cortical dynamics during fatal seizures in Cacna1a S218L mice
Abstract
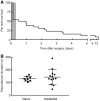
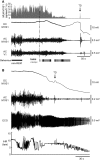
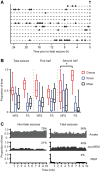
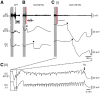
Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) is a fatal complication of epilepsy in which brainstem spreading depolarization may play a pivotal role, as suggested by animal studies. However, patiotemporal details of spreading depolarization occurring in relation to fatal seizures have not been investigated. In addition, little is known about behavioural and neurophysiological features that may discriminate spontaneous fatal from non-fatal seizures. Transgenic mice carrying the missense mutation S218L in the α1A subunit of Cav2.1 (P/Q-type) Ca2+ channels exhibit enhanced excitatory neurotransmission and increased susceptibility to spreading depolarization. Homozygous Cacna1aS218L mice show spontaneous non-fatal and fatal seizures, occurring throughout life, resulting in reduced life expectancy. To identify characteristics of fatal and non-fatal spontaneous seizures, we compared behavioural and electrophysiological seizure dynamics in freely-behaving homozygous Cacna1aS218L mice. To gain insight on the role of brainstem spreading depolarization in SUDEP, we studied the spatiotemporal distribution of spreading depolarization in the context of seizure-related death. Spontaneous and electrically-induced seizures were investigated by video monitoring and electrophysiological recordings in freely-behaving Cacna1aS218L and wild-type mice. Homozygous Cacna1aS218L mice showed multiple spontaneous tonic-clonic seizures and died from SUDEP in adulthood. Death was preceded by a tonic-clonic seizure terminating with hindlimb clonus, with suppression of cortical neuronal activity during and after the seizure. Induced seizures in freely-behaving homozygous Cacna1aS218L mice were followed by multiple spreading depolarizations and death. In wild-type or heterozygous Cacna1aS218L mice, induced seizures and spreading depolarization were never followed by death. To identify temporal and regional features of seizure-induced spreading depolarization related to fatal outcome, diffusion-weighted MRI was performed in anaesthetized homozygous Cacna1aS218L and wild-type mice. In homozygous Cacna1aS218L mice, appearance of seizure-related spreading depolarization in the brainstem correlated with respiratory arrest that was followed by cardiac arrest and death. Recordings in freely-behaving homozygous Cacna1aS218L mice confirmed brainstem spreading depolarization during spontaneous fatal seizures. These data underscore the value of the homozygous Cacna1aS218L mouse model for identifying discriminative features of fatal compared to non-fatal seizures, and support a key role for cortical neuronal suppression and brainstem spreading depolarization in SUDEP pathophysiology.
Figures



Comment in
-
Brainstem spreading depolarization: rapid descent into the shadow of SUDEP.Brain. 2019 Feb 1;142(2):231-233. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy356. Brain. 2019. PMID: 30698758 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Apnea Associated with Brainstem Seizures in Cacna1aS218L Mice Is Caused by Medullary Spreading Depolarization.J Neurosci. 2019 Nov 27;39(48):9633-9644. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1713-19.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 18. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31628185 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperexcitable superior colliculus and fatal brainstem spreading depolarization in a model of Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy.Brain Commun. 2022 Jan 19;4(2):fcac006. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac006. eCollection 2022. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 35474853 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous and optogenetically induced cortical spreading depolarization in familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 mutant mice.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Mar;192:106405. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106405. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Neurobiol Dis. 2024. PMID: 38211710
-
Genetic and Cellular Mechanisms Underlying SUDEP Risk.In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Vezzani A, Delgado-Escueta AV, editors. Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies. 5th edition. New York: Oxford University Press; 2024. Chapter 63. In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Vezzani A, Delgado-Escueta AV, editors. Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies. 5th edition. New York: Oxford University Press; 2024. Chapter 63. PMID: 39637214 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Perspectives on the basis of seizure-induced respiratory dysfunction.Front Neural Circuits. 2022 Dec 20;16:1033756. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2022.1033756. eCollection 2022. Front Neural Circuits. 2022. PMID: 36605420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Genotype to Phenotype: Expanding the Clinical Spectrum of CACNA1A Variants in the Era of Next Generation Sequencing.Front Neurol. 2021 Mar 2;12:639994. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.639994. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33737904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The de novo CACNA1A pathogenic variant Y1384C associated with hemiplegic migraine, early onset cerebellar atrophy and developmental delay leads to a loss of Cav2.1 channel function.Mol Brain. 2021 Feb 8;14(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00745-2. Mol Brain. 2021. PMID: 33557884 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal infarction and generalized seizures predict early mortality after endovascular middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice.Exp Neurol. 2024 Oct;380:114903. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114903. Epub 2024 Jul 28. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39079623
-
Causes and Effects Contributing to Sudden Death in Epilepsy and the Rationale for Prevention and Intervention.Front Neurol. 2020 Jul 31;11:765. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00765. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32849221 Free PMC article.
-
Apnea Associated with Brainstem Seizures in Cacna1aS218L Mice Is Caused by Medullary Spreading Depolarization.J Neurosci. 2019 Nov 27;39(48):9633-9644. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1713-19.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 18. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31628185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexandre V, Mercedes B, Valton L, Maillard L, Bartolomei F, Szurhaj W et al. . Risk factors of postictal generalized EEG suppression in generalized convulsive seizures. Neurology 2015; 85(18): 1598–603. - PubMed
-
- Bagnall RD, Crompton DE, Petrovski S, Lam L, Cutmore C, Garry SI et al. . Exome-based analysis of cardiac arrhythmia, respiratory control, and epilepsy genes in sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. Ann Neurol 2016; 79(4): 522–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

