Night-time systolic blood pressure and subclinical cerebrovascular disease: the Cardiovascular Abnormalities and Brain Lesions (CABL) study
- PMID: 30649236
- PMCID: PMC6587117
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjci/jey221
Night-time systolic blood pressure and subclinical cerebrovascular disease: the Cardiovascular Abnormalities and Brain Lesions (CABL) study
Abstract
Aims: Although ambulatory blood pressure (BP) is a better predictor of cardiovascular outcomes than office BP, its association with subclinical cerebrovascular disease is not clarified. We investigated the associations of office and ambulatory BP values with subclinical cerebrovascular disease in a population based, predominantly elderly cohort without prior stroke.
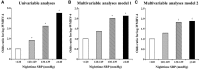
Methods and results: Eight hundred and twenty-eight participants underwent 24-h ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM), 2D echocardiography and brain magnetic resonance imaging in the Cardiac Abnormalities and Brain Lesion (CABL) study. Daytime, night-time, and 24-h BPs, nocturnal dipping pattern, morning surge (MS), and 24-h variability were assessed. Subclinical cerebrovascular disease was defined as silent brain infarcts (SBIs) and white matter hyperintensity volume (WMHV). The association of BP measures with the presence of SBI and upper quartile of log-WMHV (log-WMHV4) was analysed. SBIs were detected in 111 patients (13.4%). Mean log-WMHV was -0.99 ± 0.94. In multivariable analysis, only night-time systolic BP (SBP) was significantly associated with SBI [odds ratio (OR) 1.15 per 10 mmHg, P = 0.042], independent of cardiovascular risk factors, and pertinent echocardiographic parameters. Although daytime, night-time, 24-h BPs, and non-dipping pattern were all significantly associated with log-WMHV4 (all P < 0.05), night-time SBP showed the strongest association (OR 1.21 per 10 mmHg, P = 0.003) and was the sole independent predictor when tested against the other BP parameters. Office BP measures, MS, and BP variability were not associated with subclinical cerebrovascular disease in adjusted analyses.
Conclusion: Elevated night-time SBP is strongly associated with subclinical cerebrovascular disease. Night-time SBP by ABPM allows to identify individuals at higher risk of hypertensive brain injury.
Keywords: ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; night-time blood pressure; silent brain infarcts; white matter hyperintensity.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2019. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J.. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005;365:217–23. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, D'Agostino RB, Belanger AJ, Wolf PA, Levy D.. Left atrial size and the risk of stroke and death. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1995;92:835–41. - PubMed
-
- Di Tullio MR, Sacco RL, Sciacca RR, Homma S.. Left atrial size and the risk of ischemic stroke in an ethnically mixed population. Stroke 1999;30:2019–24. - PubMed
-
- Gardin JM, McClelland R, Kitzman D, Lima JA, Bommer W, Klopfenstein HS. et al. M-mode echocardiographic predictors of six- to seven-year incidence of coronary heart disease, stroke, congestive heart failure, and mortality in an elderly cohort (the Cardiovascular Health Study). Am J Cardiol 2001;87:1051–7. - PubMed
-
- Hansen TW, Li Y, Boggia J, Thijs L, Richart T, Staessen JA.. Predictive role of the nighttime blood pressure. Hypertension 2011;57:3–10. - PubMed

