Imaging and diagnostic advances for intracranial meningiomas
- PMID: 30649491
- PMCID: PMC6347083
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noy143
Imaging and diagnostic advances for intracranial meningiomas
Abstract
The archetypal imaging characteristics of meningiomas are among the most stereotypic of all central nervous system (CNS) tumors. In the era of plain film and ventriculography, imaging was only performed if a mass was suspected, and their results were more suggestive than definitive. Following more than a century of technological development, we can now rely on imaging to non-invasively diagnose meningioma with great confidence and precisely delineate the locations of these tumors relative to their surrounding structures to inform treatment planning. Asymptomatic meningiomas may be identified and their growth monitored over time; moreover, imaging routinely serves as an essential tool to survey tumor burden at various stages during the course of treatment, thereby providing guidance on their effectiveness or the need for further intervention. Modern radiological techniques are expanding the power of imaging from tumor detection and monitoring to include extraction of biologic information from advanced analysis of radiological parameters. These contemporary approaches have led to promising attempts to predict tumor grade and, in turn, contribute prognostic data. In this supplement article, we review important current and future aspects of imaging in the diagnosis and management of meningioma, including conventional and advanced imaging techniques using CT, MRI, and nuclear medicine.
Figures



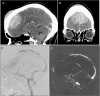
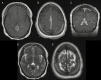
References
-
- Cushing H. Meningiomas. Springfield, IL: Thomas; 1938.
-
- Mills CK, Pfahler GE. Tumor of the brain localized clinically and by the roentgen rays. PMJ. 1902;9:268–273.
-
- Sosman MC, Putnam TJ. Roentgenological aspects of brain tumors: meningiomas. Am J Roentgenol. 1925;13:1–12.
-
- Moniz EP, Pinto A, Lima A. Le diagnostic differentiel entre les meningiomes et les autres tumeurs cerebrales par l’epreuve de l’encephalographie arterielle. Revista de Neurologia. 1929;1:1126–1135.
-
- List CF, Hodges FJ. Differential diagnosis of intracranial neoplasms by cerebral angiography. Radiology. 1947;48(5):493–508. - PubMed

