Short-course, oral flubendazole does not mediate significant efficacy against Onchocerca adult male worms or Brugia microfilariae in murine infection models
- PMID: 30650071
- PMCID: PMC6334903
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006356
Short-course, oral flubendazole does not mediate significant efficacy against Onchocerca adult male worms or Brugia microfilariae in murine infection models
Abstract
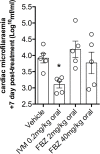
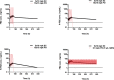
The Onchocerca ochengi adult implant and Brugia malayi microfilariemic Severe-Combined Immunodeficient (SCID) mouse models are validated screens to measure macrofilaricidal and microfilaricidal activities of candidate onchocerciasis drugs. The purpose of this study was to assess whether 5 daily sub-cutaneous (s.c.) injections of standard flubendazole (FBZ) suspension (10mg/kg), a single s.c. injection (10mg/kg) or 5 daily repeated oral doses of FBZ amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) formulation (0.2, 1.5 or 15mg/kg) mediated macrofilaricidal efficacy against O. ochengi male worms implanted into SCID mice. The direct microfilaricidal activity against circulating B. malayi microfilariae of single dose FBZ ASD formulation (2 or 40 mg/kg) was also evaluated and compared against the standard microfilaricide, ivermectin (IVM). Systemic exposures of FBZ/FBZ metabolites achieved following dosing were measured by pharmacokinetic (PK) bioanalysis. At necropsy, five weeks following start of FBZ SC injections, there were significant reductions in burdens of motile O. ochengi worms following multiple injections (93%) or single injection (82%). Further, significant proportions of mice dosed following multiple injections (5/6; 83%) or single injection (6/10; 60%) were infection negative (drug-cured). In comparison, no significant reduction in recovery of motile adult O. ochengi adult worms was obtained in any multiple-oral dosage group. Single oral-dosed FBZ did not mediate any significant microfilaricidal activity against circulating B. malayi mf at 2 or 7 days compared with >80% efficacy of single dose IVM. In conclusion, multiple oral FBZ formulation doses, whilst achieving substantial bioavailability, do not emulate the efficacy delivered by the parenteral route in vivo against adult O. ochengi. PK analysis determined FBZ efficacy was related to sustained systemic drug levels rather than achievable Cmax. PK modelling predicted that oral FBZ would have to be given at low dose for up to 5 weeks in the mouse model to achieve a matching efficacious exposure profile.
Conflict of interest statement
Sophie Lachaud, Fetene Tekle, Ludo Quirynen, Marc Engelen, and Benny Baeten are paid employees of Janssen, developed flubendazole and hold patent applications for flubendazole. Joseph D. Turner and Mark J. Taylor received funding for this study by Janssen.
Figures

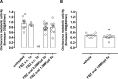
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of subcutaneous doses and a new oral amorphous solid dispersion formulation of flubendazole on male jirds (Meriones unguiculatus) infected with the filarial nematode Brugia pahangi.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Jan 16;13(1):e0006787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006787. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 30650084 Free PMC article.
-
A murine macrofilaricide pre-clinical screening model for onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis.Parasit Vectors. 2014 Oct 24;7:472. doi: 10.1186/s13071-014-0472-z. Parasit Vectors. 2014. PMID: 25338621 Free PMC article.
-
Macrofilaricidal efficacy of single and repeated oral and subcutaneous doses of flubendazole in Litomosoides sigmodontis infected jirds.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Jan 16;13(1):e0006320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006320. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 30650105 Free PMC article.
-
Flubendazole as a macrofilaricide: History and background.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Jan 16;13(1):e0006436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006436. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 30650160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research notes from the Onchocerciasis Chemotherapy Research Centre, Ghana.Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1997 Oct;91(7):703-11. doi: 10.1080/00034989760437. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1997. PMID: 9625924 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of immune responses to Loa loa stage-specific antigen extracts in Loa loa-exposed BALB/c mice upon clearance of infection.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Feb 7;13(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-3921-x. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32033624 Free PMC article.
-
NKp46+ natural killer cells develop an activated/memory-like phenotype and contribute to innate immunity against experimental filarial infection.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 27;13:969340. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.969340. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36238293 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of subcutaneous doses and a new oral amorphous solid dispersion formulation of flubendazole on male jirds (Meriones unguiculatus) infected with the filarial nematode Brugia pahangi.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Jan 16;13(1):e0006787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006787. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 30650084 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophils in filarial infections: Inducers of protection or pathology?Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 31;13:983812. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.983812. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eosinophil-Mediated Immune Control of Adult Filarial Nematode Infection Can Proceed in the Absence of IL-4 Receptor Signaling.J Immunol. 2020 Aug 1;205(3):731-740. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901244. Epub 2020 Jun 22. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32571840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meeting of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication, January 2014. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2014;89(15):153–60. - PubMed
-
- [APOC] APfOC. Final communiqué Joint Action Forum (JAF) of APOC; Paris, France2005.
-
- WHO. Onchocerciasis Factsheet No 374. 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

