A high-throughput whole cell screen to identify inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 30650074
- PMCID: PMC6334966
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205479
A high-throughput whole cell screen to identify inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
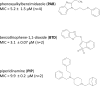
Tuberculosis is a disease of global importance for which novel drugs are urgently required. We developed a whole-cell phenotypic screen which can be used to identify inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth. We used recombinant strains of virulent M. tuberculosis which express far-red fluorescent reporters and used fluorescence to monitor growth in vitro. We optimized our high throughput assays using both 96-well and 384-well plates; both formats gave assays which met stringent reproducibility and robustness tests. We screened a compound set of 1105 chemically diverse compounds previously shown to be active against M. tuberculosis and identified primary hits which showed ≥ 90% growth inhibition. We ranked hits and identified three chemical classes of interest-the phenoxyalkylbenzamidazoles, the benzothiophene 1-1 dioxides, and the piperidinamines. These new compound classes may serve as starting points for the development of new series of inhibitors that prevent the growth of M. tuberculosis. This assay can be used for further screening, or could easily be adapted to other strains of M. tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Tanya Parish serves on the Editorial Board of PLOS ONE. This does not alter the authors' adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2017.
-
- Galandrin S, Guillet V, Rane RS, Leger M, N R, Eynard N, et al. Assay development for identifying inhibitors of the mycobacterial FadD32 activity. J Biomolec Screen. 2013;18(5):576–87. - PubMed
-
- Humnabadkar V, Jha RK, Ghatnekar N, De Sousa SM. A high-throughput screening assay for simultaneous selection of inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (Dxs) or 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase (Dxr). J Biomolec Screen. 2011;16(3):303–12. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Casey A, Odingo J, Kesicki EA, Abrahams G, Vieth M, et al. A high-throughput screen against pantothenate synthetase (PanC) identifies 3-biphenyl-4-cyanopyrrole-2-carboxylic acids as a new class of inhibitor with activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLOS One. 2013;8(11):e72786 10.1371/journal.pone.0072786 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

