Sexual and reproductive health literacy of school adolescents in Lao PDR
- PMID: 30650100
- PMCID: PMC6334956
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209675
Sexual and reproductive health literacy of school adolescents in Lao PDR
Abstract
Rationale: Adolescent pregnancy in Lao PDR is the highest in Southeast Asia. It leads to negative health and social consequences in young people. It is anticipated that this problem is partly caused by limited sexual and reproductive health literacy (SRHL), leading to poor sexual and reproductive health (SRH) decisions. Based on the concept of health literacy, SRHL goes beyond knowledge and behavior and is the self-perceived ability of an individual to access the needed information, understand the information, appraise and apply the information into informed decision making for a good way to contribute to sexual and reproductive health. It is not only knowing (knowledge) and doing (behavior), but it is the process of individual's thought on an SRH problem before taking an action. The aim of this study was to measure SRHL among school-going adolescents aged 15-19 and to determine factors associated with SRHL.
Method: We conducted a cross-sectional study in rural and urban areas of Lao PDR in 2017. Respondents completed a self-administered questionnaire with five parts: socio-demographic, personal health, SRH knowledge and behavior, SRHL, and functional literacy. We calculated the SRHL score based on the HL-EU index and used descriptive statistics to determine the score and levels. Then we used bivariate statistics and multiple linear regression to identify factors associated with SRHL in these adolescents.
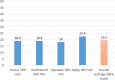
Result: Among 461 respondents, 65.5% had inadequate SRHL. Scores were positively and significantly associated with several factors, including: school location (β: 3.218; p<0.001), knowledge on SRH and attending SR class in school (p:0.010-p<0.001), and functional literacy on condoms, which reflected how respondents understood the use of condoms (β: 0.871; p<0.001).
Conclusion: Because most school adolescents had inadequate SRHL, comprehensive sexual education and enabling information as well as service access for adolescents are essential to ensure that adolescents can access, understand, appraise and apply good SRH knowledge in decision-making to benefit their own health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations Population Fund. How our future depends on a girl at this decisive age. State of world population 2016; Chap 1–3. https://www.unfpa.org/swop-2016.
-
- World Health Organization. Early marriages, adolescent and young pregnancies Report No. Sixty-fifth world health assembly 2012; Provisional agenda item 13.4, WHO, Geneva.
-
- Ganchimeg T, Mori R, Ota E, Koyanagi A, Gilmour S, Shibuya K, et al. Maternal and perinatal outcomes among nulliparous adolescents in low- and middle-income countries: a multi-country study. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2013; 120, 1622–1630, 10.1111/1471-0528.12391 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hulton LJ. Adolescent Sexual Decision-Making: An Integrative Review. The online journal of knowledge synthesis for nursing 2001; 8, 4 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials