Design, expression and functional characterization of a thermostable xylanase from Trichoderma reesei
- PMID: 30650138
- PMCID: PMC6334952
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210548
Design, expression and functional characterization of a thermostable xylanase from Trichoderma reesei
Abstract
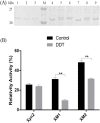
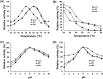
Xylanases isolated from microorganisms such as the Trichoderma reesei have attracted considerable research interest because of their potential in various industrial applications. However, naturally isolated xylanases cannot withstand harsh conditions such as high temperature and basic pH. In this study, we performed structural analysis of the major T. reesei xylanase (Xyn2), and novel flexible regions of the enzyme were identified based on B-factor, a molecular dynamics (MD) parameter. To improve thermostability of the Xyn2, disulfide bonds were introduced into the unstable flexible region by using site-directed mutagenesis and two recombinant xylanases, XM1 (Xyn2Cys12-52) and XM2 (Xyn2Cys59-149) were successfully expressed in Pichia pastoris. Secreted recombinant Xyn2 was estimated by SDS-PAGE to be 24 kDa. Interestingly, the half-lives of XM1 and XM2 at 60°C were 2.5- and 1.8- fold higher, respectively than those of native Xyn2. The XM1 also exhibited improved pH stability and maintained more than 60% activity over pH values ranging from 2.0 to 10.0. However, the specific activity and catalytic efficiency of XM1 was decreased as compared to those of XM2 and native Xyn2. Our results will assist not only in elucidating of the interactions between protein structure and function, but also in rational target selection for improving the thermostability of enzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Puls J, Schusell J (1993) Chemistry of hemicelluloses: relationship between hemicellulose structure and enzymes required for hydryolsis, p.1–27. In Coughlan MP and Hazlewood GP (ed.), Hemicellulose and hemicelluloases. Portland Press, London.
-
- Beg QK, Kapoor M, Mahajan L, Hoondal GS (2001) Microbial xylanases and their industrial applications: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:326–338. - PubMed
-
- Jun H, Jia Y, Li W, Bing Y, Daiwen C (2010) Functional characterization of a recombinant xylanase from Pichia pastoris and effect of the enzyme on nutrient digestibility in weaned pigs. Brit J Nutr 203: 1507–1513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

