Perinatal Interactions between the Microbiome, Immunity, and Neurodevelopment
- PMID: 30650376
- PMCID: PMC6447295
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.11.016
Perinatal Interactions between the Microbiome, Immunity, and Neurodevelopment
Abstract
The microbiome modulates host immune function across the gastrointestinal tract, peripheral lymphoid organs, and central nervous system. In this review, we highlight emerging evidence that microbial effects on select immune phenotypes arise developmentally, where the maternal and neonatal microbiome influence immune cell ontogeny in the offspring during gestation and early postnatal life. We further discuss roles for the perinatal microbiome and early-life immunity in regulating normal neurodevelopmental processes. In addition, we examine evidence that abnormalities in microbiota-neuroimmune interactions during early life are associated with altered risk of neurological disorders in humans. Finally, we conclude by evaluating the potential implications of microbiota-immune interventions for neurological conditions. Continued progress toward dissecting mechanistic interactions between the perinatal microbiota, immune system, and nervous system might uncover fundamental insights into how developmental interactions across physiological systems inform later-life health and disease.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
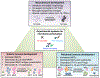

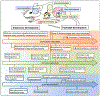
References
-
- Ahn J, Lee J, and Kim S (2015). Interferon-gamma inhibits the neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells by inhibiting the expression of Neurogenin2 via the JAK/STAT1 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 466, 52–59. - PubMed
-
- Aliprantis AO, Yang RB, Mark MR, Suggett S, Devaux B, Radolf JD, Klimpel GR, Godowski P, and Zychlinsky A (1999). Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through toll-like receptor-2. Science 285, 736–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

