Lateral Transport of Organic and Inorganic Solutes
- PMID: 30650538
- PMCID: PMC6358943
- DOI: 10.3390/plants8010020
Lateral Transport of Organic and Inorganic Solutes
Abstract
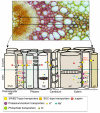
Organic (e.g., sugars and amino acids) and inorganic (e.g., K⁺, Na⁺, PO₄2-, and SO₄2-) solutes are transported long-distance throughout plants. Lateral movement of these compounds between the xylem and the phloem, and vice versa, has also been reported in several plant species since the 1930s, and is believed to be important in the overall resource allocation. Studies of Arabidopsis thaliana have provided us with a better knowledge of the anatomical framework in which the lateral transport takes place, and have highlighted the role of specialized vascular and perivascular cells as an interface for solute exchanges. Important breakthroughs have also been made, mainly in Arabidopsis, in identifying some of the proteins involved in the cell-to-cell translocation of solutes, most notably a range of plasma membrane transporters that act in different cell types. Finally, in the future, state-of-art imaging techniques should help to better characterize the lateral transport of these compounds on a cellular level. This review brings the lateral transport of sugars and inorganic solutes back into focus and highlights its importance in terms of our overall understanding of plant resource allocation.
Keywords: inorganic solutes; lateral transport; organic solutes; phloem; xylem.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Van Bel A.J.E. Xylem-phloem exchange via the rays: The undervalued route of transport. J. Exp. Bot. 1990;41:631–644. doi: 10.1093/jxb/41.6.631. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

