IL (Interleukin)-33 Suppresses Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Enhancing Regulatory T-Cell Expansion and Activity
- PMID: 30651000
- PMCID: PMC6393188
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.312023
IL (Interleukin)-33 Suppresses Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Enhancing Regulatory T-Cell Expansion and Activity
Abstract
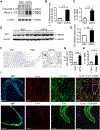
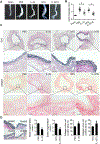
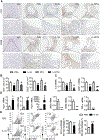
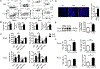
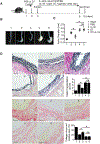
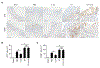
Objective- Inflammation occurs during the progression of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). IL (interleukin)-33 is a pleiotropic cytokine with multiple immunomodulatory effects, yet its role in AAA remains unknown. Approach and Results- Immunoblot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescent staining revealed increased IL-33 expression in adventitia fibroblasts from mouse AAA lesions. Daily intraperitoneal administration of recombinant IL-33 or transgenic IL-33 expression ameliorated periaorta CaPO4 injury- and aortic elastase exposure-induced AAA in mice, as demonstrated by blunted aortic expansion, reduced aortic wall elastica fragmentation, enhanced AAA lesion collagen deposition, attenuated T-cell and macrophage infiltration, reduced inflammatory cytokine production, skewed M2 macrophage polarization, and reduced lesion MMP (matrix metalloproteinase) expression and cell apoptosis. Flow cytometry analysis, immunostaining, and immunoblot analysis showed that exogenous IL-33 increased CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in spleens, blood, and aortas in periaorta CaPO4-treated mice. Yet, ST2 deficiency muted these IL-33 activities. Regulatory T cells from IL-33-treated mice also showed significantly stronger activities in suppressing smooth muscle cell inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression, macrophage MMP expression, and in increasing M2 macrophage polarization than those from vehicle-treated mice. In contrast, IL-33 failed to prevent AAA and lost its beneficial activities in CaPO4-treated mice after selective depletion of regulatory T cells. Conclusions- Together, this study established a role of IL-33 in protecting mice from AAA formation by enhancing ST2-dependent aortic and systemic regulatory T-cell expansion and their immunosuppressive activities.
Keywords: T lymphocytes, regulatory; animals; aortic aneurysm, abdominal; interleukin-33; mice.
Figures
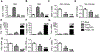
Comment in
-
Lost in translation: do animal studies add value to the management of abdominal aortic aneurysms?J Thorac Dis. 2019 May;11(Suppl 9):S1277-S1278. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.04.110. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31245108 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
IL-33 in murine abdominal aortic aneurysm: a novel inflammatory mediator awaiting clinical translation.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Jun;11(6):2181-2184. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.06.20. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31372246 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Nordon IM, Hinchliffe RJ, Loftus IM, Thompson MM. Pathophysiology and epidemiology of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011;8:92–102. - PubMed
-
- Hellenthal FA, Buurman WA, Wodzig WK, Schurink GW. Biomarkers of AAA progression. Part 1: extracellular matrix degeneration. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2009;6:464–474. - PubMed
-
- Hellenthal FA, Buurman WA, Wodzig WK, Schurink GW. Biomarkers of abdominal aortic aneurysm progression. Part 2: inflammation. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2009;6:543–552. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu K, Mitchell RN, Libby P. Inflammation and cellular immune responses in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006; 26(5): 987–994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

