Genetic and lifestyle risk factors for MRI-defined brain infarcts in a population-based setting
- PMID: 30651383
- PMCID: PMC6369905
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006851
Genetic and lifestyle risk factors for MRI-defined brain infarcts in a population-based setting
Abstract
Objective: To explore genetic and lifestyle risk factors of MRI-defined brain infarcts (BI) in large population-based cohorts.
Methods: We performed meta-analyses of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and examined associations of vascular risk factors and their genetic risk scores (GRS) with MRI-defined BI and a subset of BI, namely, small subcortical BI (SSBI), in 18 population-based cohorts (n = 20,949) from 5 ethnicities (3,726 with BI, 2,021 with SSBI). Top loci were followed up in 7 population-based cohorts (n = 6,862; 1,483 with BI, 630 with SBBI), and we tested associations with related phenotypes including ischemic stroke and pathologically defined BI.
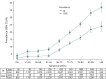
Results: The mean prevalence was 17.7% for BI and 10.5% for SSBI, steeply rising after age 65. Two loci showed genome-wide significant association with BI: FBN2, p = 1.77 × 10-8; and LINC00539/ZDHHC20, p = 5.82 × 10-9. Both have been associated with blood pressure (BP)-related phenotypes, but did not replicate in the smaller follow-up sample or show associations with related phenotypes. Age- and sex-adjusted associations with BI and SSBI were observed for BP traits (p value for BI, p [BI] = 9.38 × 10-25; p [SSBI] = 5.23 × 10-14 for hypertension), smoking (p [BI] = 4.4 × 10-10; p [SSBI] = 1.2 × 10-4), diabetes (p [BI] = 1.7 × 10-8; p [SSBI] = 2.8 × 10-3), previous cardiovascular disease (p [BI] = 1.0 × 10-18; p [SSBI] = 2.3 × 10-7), stroke (p [BI] = 3.9 × 10-69; p [SSBI] = 3.2 × 10-24), and MRI-defined white matter hyperintensity burden (p [BI] = 1.43 × 10-157; p [SSBI] = 3.16 × 10-106), but not with body mass index or cholesterol. GRS of BP traits were associated with BI and SSBI (p ≤ 0.0022), without indication of directional pleiotropy.
Conclusion: In this multiethnic GWAS meta-analysis, including over 20,000 population-based participants, we identified genetic risk loci for BI requiring validation once additional large datasets become available. High BP, including genetically determined, was the most significant modifiable, causal risk factor for BI.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Vermeer SE, Longstreth WT Jr, Koudstaal PJ. Silent brain infarcts: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 2007;6:611–619. - PubMed
-
- Longstreth WT Jr. Brain vascular disease: overt and covert. Stroke 2005;36:2062–2063. - PubMed
-
- Saini M, Ikram K, Hilal S, Qiu A, Venketasubramanian N, Chen C. Silent stroke: not listened to rather than silent. Stroke 2012;43:3102–3104. - PubMed
-
- Bernick C, Kuller L, Dulberg C, et al. Silent MRI infarcts and the risk of future stroke: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Neurology 2001;57:1222–1229. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- P30 AG053760/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 NS100605/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG049607/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- FS/14/55/30806/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- BB/F019394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/J006971/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS083633/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G1100540/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RF1 AG059421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087541/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- I 904/FWF_/Austrian Science Fund FWF/Austria
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG000538/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M013111/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G1001245/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG051504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N027558/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG008122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061796/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0701120/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG033040/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 NS100605/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001429/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources