Rapid tissue processing technique: A novel method using methyl salicylate
- PMID: 30651699
- PMCID: PMC6306597
- DOI: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_228_17
Rapid tissue processing technique: A novel method using methyl salicylate
Abstract
Introduction: Tissue processing involves transition of the biopsy tissue in graded concentration of various chemicals to make the tissue amiable for sectioning. The entire process takes 2-3 working days before a microscopic slide is ready for diagnosis. In order to shorten the turnaround time, rapid tissue processing method using methyl salicylate was developed.
Aim: The aim of this study is to develop a rapid tissue processing technique using methyl salicylate as a clearing agent and to compare it with routine tissue processing technique.
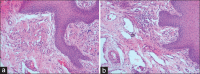
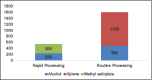
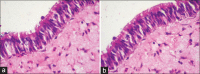
Materials and methods: A total of 70 tissue specimens were cut into two equal halves. One each was processed by routine processing technique (RoPT) and rapid processing technique (RaPT). Tissue specimens were measured before and after processing. Quality of staining and cellular-level shrinkage were observed and scored for specimens. Statistical analysis using Welch's unequal variances t-test was performed. Costs of chemicals in both the techniques were compared to see the cost-effectiveness of RaPT.
Results and conclusion: Outcomes of both the processing techniques were comparable with statistically not significant P values for all the parameters. Hence, the results of RaPT technique are satisfactory, and the use of this technique may prove beneficial to pathology laboratories.
Keywords: Methyl salicylate; rapid; routine; tissue processing; xylene.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bancroft JD, Gamble M, editors. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. 5th ed. London: Harcourt Publishers; 2002. Tissue processing and microtomy; pp. 85–92.
-
- Panja P, Sriram G, Saraswathi TR, Sivapathasundharam B. Comparison of three different methods of tissue processing. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2007;11:15–7.
-
- Rohr LR, Layfield LJ, Wallin D, Hardy D. A comparison of routine and rapid microwave tissue processing in a surgical pathology laboratory. Quality of histologic sections and advantages of microwave processing. Am J Clin Pathol. 2001;115:703–8. - PubMed
-
- Culling CF. Handbook of Histopathological and Histochemical Techniques (Including Museum Techniques) 3rd ed. Butterworth and Co: (Publishers) Ltd; 1974.
-
- [Last accessed on 2017 Oct 25]. Available from: https://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methyl_salicylate .

