Rosiglitazone metformin adduct inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via activation of AMPK/p21 pathway
- PMID: 30651718
- PMCID: PMC6330460
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-019-0732-2
Rosiglitazone metformin adduct inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via activation of AMPK/p21 pathway
Abstract
Background: Rosiglitazone metformin adduct (RZM) is a novel compound, synthesized from rosiglitazone (Ros) and metformin (Met) combined at a molar mass ratio of 1:1. Met and Ros are widely used together for treating type 2 diabetes to improve drug effectiveness and reduce adverse drug reactions. Recent studies reported that both Met and Ros may possess antineoplastic properties in several cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the effects of RZM in HCC and its underlying mechanisms remain unknown.
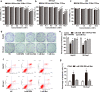
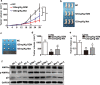
Methods: RZM was synthesized from Ros and Met at an equal molar ratio and identified by infrared spectroscopy. MTS and colony formation assays were performed to detect proliferative repression of RZM, the mixture, Met and Ros, respectively. Tumorigenesis assay in vivo was used to confirm the anti-tumorigenesis potential of RZM and Met. Moreover, cellular apoptosis caused by RZM was analyzed by hoechst staining assay and flow cytometry. RT-qPCR and western blotting were performed to reveal mechanisms for the function of RZM.
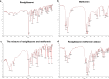
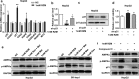
Results: Both in vitro and in vivo data showed that low doses of RZM enhanced inhibitory effect on HCC cells growth compared with Met. Flow cytometry analysis confirmed that treatment with RZM at 1 mM for 48 h triggered HCC cells apoptosis. RT-qPCR and western blotting analyses showed that p21 was upregulated in response to 1 mM RZM treatment. Furthermore, RZM could increase AMPK activation compared with Met. The increased p21 expression induced by RZM treatment was attenuated by an AMPK inhibitor compound C.
Conclusions: All these observations demonstrate that RZM increases the antiproliferative effect of Met in HCC via upregulating p21 expression in an AMPK-dependent manner. Our results suggest that RZM has the potential to be an adjuvant for HCC therapy.
Keywords: AMPK/p21 pathway; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Metformin; Proliferation; Rosiglitazone metformin adduct.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Anti-Breast Cancer Effect and Mechanism of Glimepiride-Metformin Adduct.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 4;13:3777-3788. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S240252. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32440146 Free PMC article.
-
Dual AMPK activation and TXNIP suppression underlie the superior anti-diabetic action of rosiglitazone-metformin co-crystal (RZM): evidence from preclinical models.J Drug Target. 2025 Jul 17:1-10. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2025.2534175. Online ahead of print. J Drug Target. 2025. PMID: 40658109
-
Low concentration of metformin induces a p53-dependent senescence in hepatoma cells via activation of the AMPK pathway.Int J Oncol. 2013 Nov;43(5):1503-10. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2077. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23982736
-
Prognostic significance of AMPK activation and therapeutic effects of metformin in hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Oct 1;19(19):5372-80. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0203. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23942093
-
RETRACTED: Adenine Combined with Cisplatin Promotes Anticancer Activity against Hepatocellular Cancer Cells through AMPK-Mediated p53/p21 and p38 MAPK Cascades.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jun 26;15(7):795. doi: 10.3390/ph15070795. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. Retraction in: Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 17;18(2):263. doi: 10.3390/ph18020263. PMID: 35890094 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
Metformin attenuates diabetic renal injury via the AMPK-autophagy axis.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jun;21(6):578. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10010. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33850550 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic alterations and vulnerabilities in hepatocellular carcinoma.Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2020 Nov 18;9(1):1-13. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goaa066. eCollection 2021 Jan. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2020. PMID: 33747521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Anti-Breast Cancer Effect and Mechanism of Glimepiride-Metformin Adduct.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 4;13:3777-3788. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S240252. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32440146 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Related Risk Factors and Drugs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jan 19;11:159-171. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S441672. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 38268569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving Dissolution and Cytotoxicity by Forming Multidrug Crystals.Molecules. 2020 Mar 16;25(6):1343. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061343. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32188020 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

