MicroRNA-144 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CCNB1
- PMID: 30651720
- PMCID: PMC6332595
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-019-0729-x
MicroRNA-144 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CCNB1
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies with a high morbidity and mortality worldwide. MicroRNAs are key regulators of HCC genesis. However, the regulatory role and underlying mechanisms of microRNA in HCC is still limited.
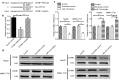
Methods: Cyclin B1 (CCNB1) mRNA levels were examined in non-tumor and liver cancer of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) cohort. CCNB1 was knockdown to evaluate the HCC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. MicroRNA-144 targeting CCNB1 was identified with TargetScan analysis and confirmed with reporter assay. Overexpression of MicroRNA-144 was achieved using microRNA mimics and function of microRNA-144 was tested in vitro HCC cell line proliferation and in vivo tumor formation experiments.
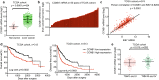
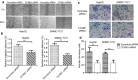
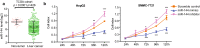
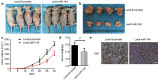
Results: Here, we found that the high level expression of CCNB1 was closely associated with poor prognosis in HCC patients. Knockdown of CCNB1 by RNA interference significantly inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion in HCC. Furthermore, we found that miR-144 directly targeted CCNB1 and inhibited CCNB1 expression. Moreover, in vivo experiments of subcutaneous tumor formation further demonstrated that miR-144 delayed tumor formation by negative regulation of CCNB1.
Conclusion: Therefore, we conclude that microRNA-144/CCNB1 axis plays an important role in human HCC. Therapies targeting microRNA-144 could potentially improve HCC treatment.
Keywords: CCNB1; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Invasion; MicroRNA-144; Migration; Proliferation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RP11-295G20.2 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the miR-6884-3p/CCNB1 pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jul 20;12(14):14918-14932. doi: 10.18632/aging.103552. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32687483 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1 promotes proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by transcriptional activation of CCNB1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jun 12;500(4):924-929. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.201. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29705704
-
Huanglian decoction suppresses the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by reducing CCNB1 expression.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Mar 14;27(10):939-958. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i10.939. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33776365 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-183-5p contributes to malignant progression through targeting PDCD4 in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2020 Oct 30;40(10):BSR20201761. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201761. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33078826 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-98-5p Inhibits Tumorigenesis of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting NF-κB-Inducing Kinase.Yonsei Med J. 2020 Jun;61(6):460-470. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.6.460. Yonsei Med J. 2020. PMID: 32469170 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential of modern circulating cell-free DNA diagnostic tools for detection of specific tumour cells in clinical practice.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2020 Oct 15;30(3):030504. doi: 10.11613/BM.2020.030504. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2020. PMID: 32774122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics screening the novel and promising targets of curcumin in hepatocellular carcinoma chemotherapy and prognosis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jan 25;22(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03487-9. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35078445 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MiRNA in Cancer: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2257:375-422. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1170-8_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34432288
-
MicroRNA, mRNA, and Proteomics Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Improving Lung Cancer Treatment Outcomes.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 14;15(8):2294. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082294. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190222 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, and candidate targeted agents for hepatitis B virus-associated early stage hepatocellular carcinoma based on RNA-sequencing data.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):231. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12094. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32968453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nimeus-Malmstrom E, Koliadi A, Ahlin C, Holmqvist M, Holmberg L, Amini RM, Jirstrom K, Warnberg F, Blomqvist C, Ferno M, et al. Cyclin B1 is a prognostic proliferation marker with a high reproducibility in a population-based lymph node negative breast cancer cohort. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(4):961–967. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

