Effect of rosuvastatin on vascular endothelial functions and inflammatory factors of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease
- PMID: 30651799
- PMCID: PMC6307424
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6923
Effect of rosuvastatin on vascular endothelial functions and inflammatory factors of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease
Abstract
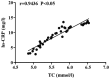
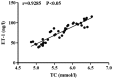
Effects of rosuvastatin on vascular endothelial functions and inflammatory factors of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease were investigated. Eighty patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease, who were admitted and treated in Center hospital of Zibo from January 2016 to January 2017, were selected and divided into observation group (n=40) and control group (n=40) by the random number table; symptomatic and supporting therapy, including use of metformin, captopril, asprin and levocarnitine, was used in control group while rosuvastatin was adopted in observation group in addition to the symptomatic and supporting therapy. Patients in both groups were treated for a treatment cycle, namely, 3 consecutive months. After that, indexes related to blood lipid, diabetes mellitus and vascular endothelial activity, as well as variations in inflammation-associated cytokines, before and after intervention were compared; the correlation of changes in total cholesterol (TC) with those in fasting insulin (FINS), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and endothelin-1 (ET-1), respectively, was analyzed. Among the blood lipid indexes of the patients, the levels of TC, triglyceride (TG) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) after intervention were significantly lower than those before intervention (P<0.05), while the post-intervention level of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) was higher than that before intervention (P<0.05). Compared with those before intervention, the level of FINS after intervention was remarkably higher (P<0.05), while the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) level after intervention was significantly lower (P<0.05). After intervention, the levels of hs-CRP and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the patients were obviously decreased compared with those before intervention (P<0.05). Compared with that before intervention, the ET-1 level was decreased (P<0.05), while the nitric oxide (NO) level was elevated after intervention (P<0.05). The TC level was negatively correlated with FINS level (P<0.05) but positively correlated with the levels of hs-CRP (P<0.05) and ET-1 (P<0.05). For patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease, treatment with rosuvastatin can effectively lower the level of blood lipid and regulate insulin functions; moreover, potent decrease in blood lipid level has great significance in improving the vascular endothelial functions and reducing inflammatory response levels.
Keywords: correlation research; inflammatory factors; patients with coronary heart disease; rosuvastatin; type 2 diabetes mellitus; vascular endothelial functions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of telmisartan on vascular endothelial function, inflammation and insulin resistance in patients with coronary heart disease and diabetes mellitus.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jan;15(1):909-913. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5451. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29399098 Free PMC article.
-
A study of the correlation of insulin resistance and leptin with inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial injury in T2DM patients with CHD.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jul;16(1):265-269. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6170. Epub 2018 May 16. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29896248 Free PMC article.
-
[Correlation of retinol binding protein 4 with metabolic indexes of glucose and lipid, bile cholesterol saturation index].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 Jun;40(6):657-65. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2015.06.014. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015. PMID: 26164516 Chinese.
-
Expression of C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP3) in serum of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus and its relationship with insulin resistance.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Dec;21(24):5702-5710. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201712_14016. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29272006
-
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and atherosclerotic disease: from improved risk prediction to risk-guided therapy.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Oct 15;168(6):5126-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.07.113. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23978367 Review.
Cited by
-
Stratifying risk of acute kidney injury in pre and post cardiac surgery patients using a novel biomarker-based algorithm and clinical risk score.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 18;9(1):16963. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53349-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31740699 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between Changes in Serum RBP4, hs-CRP, and IL-27 Levels and Rosuvastatin in the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Dec 15;2021:8476592. doi: 10.1155/2021/8476592. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 34956579 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of oral rosuvastatin intervention on HDL and its associated proteins in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Endocrine. 2021 Jan;71(1):76-86. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02472-5. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Endocrine. 2021. PMID: 32895874
References
-
- Kwon O, Kang SJ, Kang SH, Lee PH, Yun SC, Ahn JM, Park DW, Lee SW, Kim YH, Lee CW, et al. Relationship between serum inflammatory marker levels and the dynamic changes in coronary plaque characteristics after statin therapy. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;10:e005934. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.116.005934. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ovrakh T, Serik S, Kochubiei O. Impact of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin on residual on-clopidogrel treatment platelet reactivity in patients with ischemic heart disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus after acute coronary syndrome. Georgian Med News. 2017;4:7–14. (In Russian) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
