Restoration of miRNA-148a in pancreatic cancer reduces invasion and metastasis by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via downregulating maternally expressed gene-3
- PMID: 30651845
- PMCID: PMC6307449
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.7026
Restoration of miRNA-148a in pancreatic cancer reduces invasion and metastasis by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via downregulating maternally expressed gene-3
Abstract
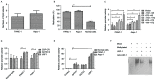
Various microRNAs (miRNA) have been recognized potential novel tumor markers and have a critical role in cancer development and progression. Recently, methylation of miRNA-148a was identified as a crucial biochemical process in the progression of cancer. However, its potential role and in pancreatic cancer as well as the underlying mechanisms have remained largely elusive. The present study investigated the potential antitumor effect of miR-148a as well as its impact on invasion and metastasis in pancreatic cancer. It was found that the expression of miRNA-148a and the potential predictive biomarker maternally expressed gene-3 (MEG-3) were obviously decreased in human pancreatic cancer tissues compared with those in adjacent non-tumorous tissues. Furthermore, miR-148a was found to be downregulated in pancreatic cancer cell lines compared with normal pancreatic cells through promoter methylation. An MTT assay and a clonogenic assay demonstrated that restoration of miRNA-148a inhibited the proliferation and colony formation of pancreatic cancer cells. In addition, miR-148a transduction led to the upregulation of MEG-3 expression and promoted apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. Western blot analysis revealed that transduction of miR-148a markedly decreased the expression levels of C-myc, cyclin D1 and β-catenin in pancreatic cancer cells. Methylation of miR-148a not only decreased the endogenous β-catenin levels but also inhibited the nuclear translocation of β-catenin to delay cell cycle progression. Furthermore, ectopic miR-148a methylation inhibited pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion via causing an upregulation of MEG-3 expression. Most importantly, ectopic overexpression of miR-148a in pancreatic cancer cells inhibited tumor formation in an animal experiment. Taken together, miR-148a methylation is a crucial regulatory process to inhibit the proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells, and transduction of miR-148a suppressed the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through negative regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The findings of the present study suggested that miRNA-148a acts as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer and may contribute to the development of novel treatments for pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: MEG-3; Wnt/β-catenin; metastasis; methylation; miR-148a; pancreatic cancer.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-148a suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting Wnt10b and inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jul;38(1):301-308. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5705. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Oncol Rep. 2017. Retraction in: Oncol Rep. 2023 Mar;49(3):56. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8493. PMID: 28586066 Retracted.
-
MiR-148a suppressed cell invasion and migration via targeting WNT10b and modulating β-catenin signaling in cisplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:902-909. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.080. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551544
-
MicroRNA-148a inhibits breast cancer migration and invasion by directly targeting WNT-1.Oncol Rep. 2016 Mar;35(3):1425-32. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4502. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26707142
-
The Role of Mir-148a in Cancer.J Cancer. 2016 Jun 21;7(10):1233-41. doi: 10.7150/jca.14616. eCollection 2016. J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27390598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on the Role of miR-1290 in Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis and Invasion.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Dec 24;8:763338. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.763338. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 35004844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of miR-6794-3p as a suppressor in pancreatic cancer metastasis.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Sep 30;20(13):5272-5292. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.98490. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39430246 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic and tumor suppressor function of MEIS and associated factors.Turk J Biol. 2020 Dec 14;44(6):328-355. doi: 10.3906/biy-2006-25. eCollection 2020. Turk J Biol. 2020. PMID: 33402862 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA HOTAIRM1 regulates cell proliferation and the metastasis of thyroid cancer by targeting Wnt10b.Oncol Rep. 2021 Mar;45(3):1083-1093. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7919. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33650656 Free PMC article.
-
LNC00673 suppresses proliferation and metastasis of pancreatic cancer via target miR-504/ HNF1A.J Cancer. 2020 Jan 1;11(4):940-948. doi: 10.7150/jca.32855. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31949497 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA‑7515 suppresses pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via downregulating IGF‑1 expression.Oncol Rep. 2021 Sep;46(3):200. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8151. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34296285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klompmaker S, de Rooij T, Korteweg JJ, van Dieren S, van Lienden KP, van Gulik TM, Busch OR, Besselink MG. Systematic review of outcomes after distal pancreatectomy with coeliac axis resection for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Br J Surg. 2016;103:941–949. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10148. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Li J, Zhu R, Zhang H, Zheng Y, Dai W, Wang F, Shen M, Chen K, Cheng P, et al. K-ras mutational status in cytohistological tissue as a molecular marker for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:573783. doi: 10.1155/2014/573783. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
