Association of the proliferation of lung fibroblasts with the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in neonatal rats with hyperoxia-induced lung fibrosis
- PMID: 30651853
- PMCID: PMC6307421
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6999
Association of the proliferation of lung fibroblasts with the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in neonatal rats with hyperoxia-induced lung fibrosis
Abstract
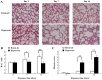
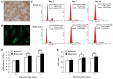
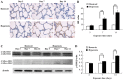
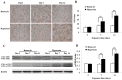
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a common, serious complication occurring in premature infants. Although clinical characteristics and pathologic changes are well described, the pathogenesis of alveolar dysplasia and interstitial fibrosis is less clear. Lung fibroblasts (LFs) are present in the extracellular matrix and serve essential roles during pulmonary epithelial injury and in response to fibrosis development in BPD. The current study investigated hyperoxia-induced proliferation of primary LFs in vitro and mechanisms that may be involved. Newborn rats were exposed to 90% oxygen, while control rats were kept in normal atmosphere. Primary LFs were isolated on postnatal day 3, 7 and 14. Hyperoxia-induced proliferation of LFs isolated on day 7 and 14 by accelerating the cell cycle progression from G1 to S phase. Collagen type I protein secretion and mRNA expression on day 7 and 14 were increased by hyperoxia compared with the controls. Hyperoxia significantly increased the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and significantly increased collagen type I expression compared with the room air control group. The findings indicated that an increase in LF proliferation in response to hyperoxia was associated with ERK1/2 phosphorylation. This mechanism may contribute to over-proliferation of LFs leading to disturbed formation of normal alveoli.
Keywords: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; fibrosis; hyperoxia; lung fibroblast.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway Activated by EGF Promotes Proliferation, Transdifferentiation, and Migration of Cultured Primary Newborn Rat Lung Fibroblasts.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 5;2020:7176169. doi: 10.1155/2020/7176169. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33083482 Free PMC article.
-
Primary culture of lung fibroblasts from hyperoxia-exposed rats and a proliferative characteristics study.Cytotechnology. 2018 Apr;70(2):751-760. doi: 10.1007/s10616-017-0179-z. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Cytotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29340836 Free PMC article.
-
5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine Inhibits the Proliferation of Lung Fibroblasts in Neonatal Rats Exposed to Hyperoxia.Pediatr Neonatol. 2017 Apr;58(2):122-127. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2015.11.009. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Pediatr Neonatol. 2017. PMID: 27663361
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying hyperoxia-induced lung fibrosis.Pediatr Neonatol. 2022 Mar;63(2):109-116. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2021.11.008. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Pediatr Neonatol. 2022. PMID: 35181258 Review.
-
In search of the elusive lipofibroblast in human lungs.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Oct 15;307(8):L605-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00230.2014. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25193605 Review.
Cited by
-
Fibroblast GSK-3α Promotes Fibrosis via RAF-MEK-ERK Pathway in the Injured Heart.Circ Res. 2022 Sep 16;131(7):620-636. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321431. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 36052698 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the p16/cyclin D1/CDK4/Rb/E2F1 pathway on aberrant lung fibroblast proliferation in neonatal rats exposed to hyperoxia.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Oct;22(4):1057. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10491. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34434271 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a novel humanized mouse model to study bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Front Pediatr. 2023 Jul 14;11:1146014. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1146014. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37520051 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications and bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jan 3;12:1426030. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1426030. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 39830627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway Activated by EGF Promotes Proliferation, Transdifferentiation, and Migration of Cultured Primary Newborn Rat Lung Fibroblasts.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 5;2020:7176169. doi: 10.1155/2020/7176169. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33083482 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
