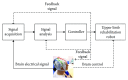
System Framework of Robotics in Upper Limb Rehabilitation on Poststroke Motor Recovery
- PMID: 30651892
- PMCID: PMC6311736
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6737056
System Framework of Robotics in Upper Limb Rehabilitation on Poststroke Motor Recovery
Abstract
Neurological impairments such as stroke cause damage to the functional mobility of survivors and affect their ability to perform activities of daily living. Recently, robotic treatment for upper limb stroke rehabilitation has received significant attention because it can provide high-intensity and repetitive movement therapy. In this review, the current status of upper limb rehabilitation robots is explored. Firstly, an overview of mechanical design of robotics for upper-limb rehabilitation and clinical effects of part robots are provided. Then, the comparisons of human-machine interactions, control strategies, driving modes, and training modes are described. Finally, the development and the possible future directions of the upper limb rehabilitation robot are discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination of Exoskeletal Upper Limb Robot and Occupational Therapy Improve Activities of Daily Living Function in Acute Stroke Patients.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019 Jul;28(7):2018-2025. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Apr 30. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 31047819 Clinical Trial.
-
A review of technological and clinical aspects of robot-aided rehabilitation of upper-extremity after stroke.Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2016;11(4):263-80. doi: 10.3109/17483107.2014.1002539. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2016. PMID: 25600057 Review.
-
Effectiveness of upper-limb robotic-assisted therapy in the early rehabilitation phase after stroke: A single-blind, randomised, controlled trial.Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2019 Sep;62(5):313-320. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2019. PMID: 31028900 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of smart force feedback rehabilitation robot training on upper limb motor function in the subacute stage of stroke.NeuroRehabilitation. 2020;47(2):209-215. doi: 10.3233/NRE-203130. NeuroRehabilitation. 2020. PMID: 32741790
-
Effects of Robot-Assisted Therapy for the Upper Limb After Stroke.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2017 Feb;31(2):107-121. doi: 10.1177/1545968316666957. Epub 2016 Sep 24. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2017. PMID: 27597165 Review.
Cited by
-
Robotics in Physical Rehabilitation: Systematic Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Aug 29;12(17):1720. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12171720. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39273744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Instance Transfer Subject-Dependent Strategy for Motor Imagery Signal Classification Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks.Comput Math Methods Med. 2020 Aug 28;2020:1683013. doi: 10.1155/2020/1683013. eCollection 2020. Comput Math Methods Med. 2020. PMID: 32908576 Free PMC article.
-
Upper limb robotic rehabilitation following stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis investigating efficacy and the influence of device features and program parameters.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2025 Jul 16;22(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12984-025-01662-4. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40671078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gait Recognition for Lower Limb Exoskeletons Based on Interactive Information Fusion.Appl Bionics Biomech. 2022 Mar 26;2022:9933018. doi: 10.1155/2022/9933018. eCollection 2022. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2022. PMID: 35378794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of the role of robots in upper limb disabilities rehabilitation: a scoping review.Arch Public Health. 2023 May 8;81(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13690-023-01100-8. Arch Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37158979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang W. Chinese stroke epidemiology and community groups to intervene. Chinese Journal of the Frontiers of Medical Science (Electronic Version) 2009;1:49–53.
-
- Zhang X. Y., Wang K. X. Robot assisted rehabilitation technology, robotics and intelligent devices. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation. 2013;28(4):246–248.
-
- Tan M., Wang S. Research progress on robotics. Acta Automatica Sinica. 2013;39(7):1119–1128.
-
- Jamwal P. K., Hussain S., Ghayesh M. H., Rogozina S. V. Impedance control of an intrinsically compliant parallel ankle rehabilitation robot. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. 2016;63(6):3638–3647. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2521600. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical