The 28-day survival rates of two cytokine-adsorbing hemofilters for continuous renal replacement therapy: a single-center retrospective comparative study
- PMID: 30651999
- PMCID: PMC6328921
- DOI: 10.1002/ams2.382
The 28-day survival rates of two cytokine-adsorbing hemofilters for continuous renal replacement therapy: a single-center retrospective comparative study
Abstract
Aim: Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) with a cytokine-adsorbing hemofilter (CAH) is effective in the treatment of sepsis. Two filter types, namely polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and surface-treated AN69 (AN69ST) hemofilters, have been successfully used for CRRT, but no direct comparisons have been published to date. This study compared the efficacy, as measured by 28-day survival rates, of PMMA and AN69ST hemofilters in patients receiving CAH-CRRT.
Methods: This retrospective observational study reviewed the medical records of 142 patients who received CAH-CRRT between November 2013 and February 2015.
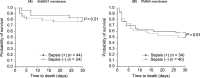
Results: The 28-day survival rates were higher in the AN69ST group than in the PMMA group for patients with or without sepsis (all patients, 79.4% versus 54.1%; patients with sepsis, 77.3% versus 50.0%; patients without sepsis, 83.3% versus 57.5%; P < 0.05). No significant differences were observed regarding 28-day survival rates of patients with or without sepsis (AN69ST, 77.3% versus 83.3%; P = 0.51; PMMA, 50.0% versus 57.5%; P = 0.61) using the same hemofilter.
Conclusion: The AN69ST hemofilter could be more effective than PMMA hemofilters for improving the survival outcomes of patients with or without sepsis.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; renal replacement therapy; retrospective study; sepsis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of the cytokine adsorption ability in continuous renal replacement therapy using polyethyleneimine-coated polyacrylonitrile (AN69ST) or polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) hemofilters: a pilot single-center open-label randomized control trial.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Jun 30;28(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01184-6. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37391846 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Polyethyleneimine-treated polyacrylonitrile membrane hemofilter for critically ill patients receiving anticoagulant-free prolonged intermittent renal replacement therapy: a single-center, prospective, self-controlled pilot study.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Jun 30;18(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0627-1. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28666474 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
In vitro Evaluation of Linezolid and Doripenem Clearance with Different Hemofilters.Blood Purif. 2020;49(3):295-301. doi: 10.1159/000504039. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Blood Purif. 2020. PMID: 31995801 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with the oXiris Hemofilter on Critically Ill Patients: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 13;11(22):6719. doi: 10.3390/jcm11226719. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36431196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-renal indications for continuous renal replacement therapy: current status in Japan.Contrib Nephrol. 2010;166:47-53. doi: 10.1159/000314851. Epub 2010 May 7. Contrib Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20472991 Review.
Cited by
-
Continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration using cytokine-adsorbing hemofilters as adjuvant therapy for anaerobic descending necrotizing mediastinitis: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2019 Jul 5;13(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s13256-019-2123-7. J Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31272492 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Purification in Patients with Sepsis Associated with Acute Kidney Injury: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 6;12(19):6388. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196388. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37835031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical efficacy of blood purification using a polymethylmethacrylate hemofilter for the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis.Acute Crit Care. 2022 Aug;37(3):398-406. doi: 10.4266/acc.2022.00192. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Acute Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 35791651 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Acute-Phase Circuit Occlusion and Blood Calcium Concentration in an Ex Vivo Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Model.Cureus. 2024 Apr 30;16(4):e59330. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59330. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38817525 Free PMC article.
-
Tocilizumab and PMX-DHP have efficacy for severe COVID-19 pneumonia.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2021 Feb 1;9:2050313X21991063. doi: 10.1177/2050313X21991063. eCollection 2021. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33796310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cinel I, Opal SM. Molecular biology of inflammation and sepsis: a primer. Crit. Care Med. 2009; 37: 291–304. - PubMed
-
- Ronco C, Bellomo R, Homel P et al Effects of different doses in continuous veno‐venous hemofiltration on outcomes of acute renal failure: a prospective randomized trial. Lancet 2000; 9223: 26–30. - PubMed
-
- Cruz DN, Antonelli M, Fumagalli R et al Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in abdominal septic shock: the EUPHAS randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009; 301: 2445–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

