Ultracentrifugation versus kit exosome isolation: nanoLC-MS and other tools reveal similar performance biomarkers, but also contaminations
- PMID: 30652024
- PMCID: PMC6331754
- DOI: 10.4155/fsoa-2018-0088
Ultracentrifugation versus kit exosome isolation: nanoLC-MS and other tools reveal similar performance biomarkers, but also contaminations
Abstract
Aim: For isolation of exosomes, differential ultracentrifugation and an isolation kit from a major vendor were compared.
Materials & methods: 'Case study' exosomes isolated from patient-derived cells from glioblastoma multiforme and a breast cancer cell line were analyzed.
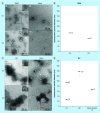
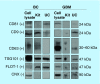
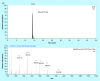
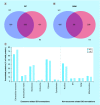
Results: Transmission electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering, western blotting, and so forth, revealed comparable performance. Potential protein biomarkers for both diseases were also identified in the isolates using nanoLC-MS. Western blotting and nanoLC-MS also revealed negative exosome markers regarding both isolation approaches.
Conclusion: The two isolation methods had an overall similar performance, but we hesitate to use the term 'exosome isolation' as impurities may be present with both isolation methods. NanoLC-MS can detect disease biomarkers in exosomes and is useful for critical assessment of exosome enrichment procedures.
Keywords: bioanalysis; exosomes; isolation.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial & competing interests disclosure Financial support from UiO:Life Science is gratefully acknowledged. This work was also partially supported by the Research Council of Norway through its Centres of Excellence scheme, project number 262613. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization and Comparison of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome Isolation Methods using Culture Supernatant.Arch Razi Inst. 2022 Aug 31;77(4):1383-1388. doi: 10.22092/ARI.2021.356141.1790. eCollection 2022 Aug. Arch Razi Inst. 2022. PMID: 36883158 Free PMC article.
-
An improvised one-step sucrose cushion ultracentrifugation method for exosome isolation from culture supernatants of mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Jul 4;9(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0923-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29973270 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study of Serum Exosome Isolation Using Differential Ultracentrifugation and Three Commercial Reagents.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 23;12(1):e0170628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170628. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28114422 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress of Exosome Isolation and Peptide Recognition-Guided Strategies for Exosome Research.Front Chem. 2022 Feb 24;10:844124. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.844124. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35281563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urine Exosomes: An Emerging Trove of Biomarkers.Adv Clin Chem. 2017;78:103-122. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Adv Clin Chem. 2017. PMID: 28057185 Review.
Cited by
-
Electromembrane Extraction and Mass Spectrometry for Liver Organoid Drug Metabolism Studies.Anal Chem. 2021 Feb 23;93(7):3576-3585. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05082. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33534551 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles, including large translating vesicles called midbody remnants, are released during the cell cycle.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Dec 1;35(12):ar155. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-10-0384. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39535882 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Exosomal and Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Promising Biomarkers in Canine Mammary Cancer.Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 1;12(4):524. doi: 10.3390/life12040524. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of precipitation and size exclusion chromatography as an effective method for exosome like extracellular vesicle isolation from pericardial fluids.Nanotheranostics. 2023 Apr 2;7(4):345-352. doi: 10.7150/ntno.82939. eCollection 2023. Nanotheranostics. 2023. PMID: 37151803 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: Delivery Vehicles of Myokines.Front Physiol. 2019 May 7;10:522. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00522. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31133872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
