The Preventive Effects of Standardized Extract of Zataria multiflora and Carvacrol on Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rat: - Zataria multiflora and Carvacrol and Hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 30652051
- PMCID: PMC6333197
- DOI: 10.3831/KPI.2018.21.028
The Preventive Effects of Standardized Extract of Zataria multiflora and Carvacrol on Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rat: - Zataria multiflora and Carvacrol and Hepatotoxicity
Abstract
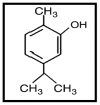
Objectives: The hepatotoxicity induced by Acetaminophen (AAP) mostly mediated by effect on oxidative stress parameters. The Zataria multiflora (Z.M) is an herbal medicine with well-known antioxidant effect. The aim of this study is investigation of preventive effects of Z.M and Carvacrol (CAR) on AAP-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.
Methods: Rats were randomly divided into four groups including: 1) Control, 2) Acetaminophen (AAP), 3) and 4) CAR. The saline, Z.M (200 mg/kg) and CAR (20 mg/kg) were administrated orally for 6 days, after that AAP (600 mg/kg) was administrated in the 7th day. Blood sampling was performed on the first and last days. Also, the liver tissue was removed for evaluation of Malondyaldehide (MDA), Thiol content, Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and Catalase (CAT). Total Protein (tPro), Glutamic Oxaloacetic Transaminase (GOT), Glutamic Pyruvic Transaminase (GPT) and Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) in liver tissue were evaluated. The changes (Δ) of enzymes activities were presented.
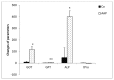
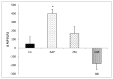
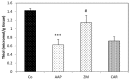
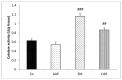
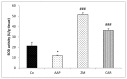
Results: The Δ GOT, Δ GPT and Δ ALP in CAR group significantly decreased compared to AAP group (P < 0.01 to P < 0.001) and Δ GPT in Z.M group was significantly reduced in comparison with AAP group (P < 0.05). Also, MDA, Thiol, SOD and CAT levels in treated groups were attenuated compared to AAP group (P < 0.05 to P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Z.M and CAR have a powerful hepatoprotective effect. CAR is more effective than Z.M. Based on the results. Z.M and CAR could be potent supplementary agents against hepatotoxicity of AAP in patients.
Keywords: Zataria multiflora; acetaminophen; carvacrol; hepatotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effects of standardized Zataria multiflora extract and its major ingredient, Carvacrol, on Adriamycin-induced hepatotoxicity in rat.Biomed J. 2018 Dec;41(6):340-347. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2018.10.008. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Biomed J. 2018. PMID: 30709575 Free PMC article.
-
Zataria multiflora extract and carvacrol affect cardiotoxicity induced by Adriamycin in rat.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2018 Dec 19;30(1):73-79. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2018-0008. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30110251
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Zataria Multiflora Boisson cisplatin-induced oxidative stress in male rat.J Med Life. 2015;8(Spec Iss 4):275-281. J Med Life. 2015. PMID: 28316744 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological effects of Zataria multiflora Boiss L. and its constituents focus on their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Feb;32(1):26-50. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12331. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29125648 Review.
-
The effect of Zataria multiflora on respiratory allergic and immunologic disorders, experimental and clinical evidence: A comprehensive review.Phytother Res. 2022 Mar;36(3):1135-1155. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7382. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 35080049 Review.
Cited by
-
The potential effect of phytochemicals and herbal plant remedies for treating drug-induced hepatotoxicity: a review.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 May;48(5):4767-4788. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06444-4. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34075538 Review.
-
Ribes khorasanicum: A Potent Antioxidant Against Organ Toxicity by Effect on the NF-κB Pathway.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Nov 11;12(12):10412-10423. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4586. eCollection 2024 Dec. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39723080 Free PMC article.
-
Zataria multiflora extract reverses lipopolysaccharide-induced anxiety and depression behaviors in rats.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2020 Jan-Feb;10(1):78-88. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2020. PMID: 31921610 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-4 can play a role in allergic rhinitis patient during treatment with Zataria multiflora.Clin Mol Allergy. 2022 Feb 10;20(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12948-022-00169-w. Clin Mol Allergy. 2022. PMID: 35144653 Free PMC article.
-
The Comparison of Antioxidant Effect of Aspirin, Metformin, Atorvastatin and Captopril Co-administration in the Heart and Kidney Tissues of Diabetic Rats.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Winter;20(1):27-39. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.112004.13481. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34400938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gunnell D, Murray V, Hawton K. Use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) for suicide and nonfatal poisoning: worldwide patterns of use and misuse. Suicide life threat behav. 2000;30(4):313–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
