Efficacy and Safety of Combination of NSAIDs and Muscle Relaxants in the Management of Acute Low Back Pain
- PMID: 30652262
- PMCID: PMC6513919
- DOI: 10.1007/s40122-019-0112-6
Efficacy and Safety of Combination of NSAIDs and Muscle Relaxants in the Management of Acute Low Back Pain
Abstract
Introduction: Low back pain is a common problem worldwide causing deterioration of health and quality of life. Low back pain is often associated with muscle spasm. We investigated the combined effect of muscle relaxants and pain killers for low back pain.
Methods: In this open-label, prospective, multicenter study, patients with acute low back pain received a single tablet of either the fixed dose combination of chlorzoxazone 500 mg and ibuprofen 400 mg (manufacturer: Dr. Reddy's Laboratories, India) (C + I group) or ibuprofen 400 mg (I group) thrice daily for up to 7 days. Primary outcomes were improvement in pain by Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Summed Pain Intensity Difference (SPID) at 3 and 7 days post-treatment.
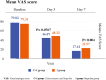
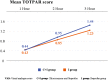
Results: A total of 406 patients were included in this study. When compared to baseline, the absolute mean change in VAS scores on Day 7 was 62.39 ± 18.78 and 57.34 ± 16.29 in the C + I and I groups, respectively (P = 0.0001). In the C + I and I groups, the mean SPID at Days 3 and 7 were 51.27 ± 24.44 and 47.80 ± 22.91, and 300.82 ± 92.40 and 277.16 ± 81.83, respectively. No deaths or serious adverse events were reported. Common adverse events included gastritis, stomach pain, fever, cold, and headache. At the end of the study, excellent to good response was reported in 94.08% and 77.33% of patients in the C + I and I groups, respectively. Excellent to good tolerability was observed in 96.05% and 89.65% patients in the two groups, respectively.
Conclusion: Fixed dose combination of chlorzoxazone and ibuprofen demonstrated superior efficacy than ibuprofen monotherapy in acute low back pain. Both drugs were well-tolerated and should be considered as judicious therapeutic options in patients with acute low back pain.
Trial registration: This trial is registered with Clinical Trial Registry of India-CTRI/2016/10/007348.
Funding: Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory agents; Chlorzoxazone; Ibuprofen; Low back pain; Non-steroidal; Spasm.
Figures
References
-
- Patrick N, Emanski E, Knaub MA. Acute and chronic low back pain. Med Clin N Am. 2014;98:777–789. - PubMed
-
- May S. Self-management of chronic low back pain and osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(4):199–209. - PubMed
-
- Dagenais S, Caro J, Haldeman S. A systematic review of low back pain cost of illness studies in the United States and internationally. Spine J. 2008;8(1):8–20. - PubMed
-
- Frydrych V. Skeletal Muscle Relaxants. Drug Class Review. 2016. https://medicaid.utah.gov/pharmacy/ptcommittee/files/Criteria%20Review%2.... Accessed on: 01 Oct, 2018.
-
- Chou R, Deyo R, Friedly J, Skelly A, Weimer M, Fu R. Systemic pharmacologic therapies for low back pain: a systematic review for an American College of Physicians Clinical Practice Guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:480–492. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources