Neuroprotective Mitochondrial Remodeling by AKAP121/PKA Protects HT22 Cell from Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 30652267
- PMCID: PMC6615994
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-018-1464-3
Neuroprotective Mitochondrial Remodeling by AKAP121/PKA Protects HT22 Cell from Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Stress
Abstract
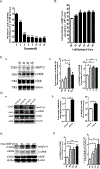
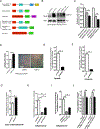
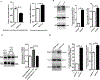
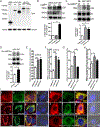
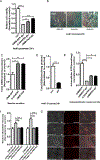
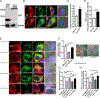
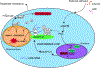
Protein kinase A (PKA) is a ser/thr kinase that is critical for maintaining essential neuronal functions including mitochondrial homeostasis, bioenergetics, neuronal development, and neurotransmission. The endogenous pool of PKA is targeted to the mitochondrion by forming a complex with the mitochondrial scaffold A-kinase anchoring protein 121 (AKAP121). Enhanced PKA signaling via AKAP121 leads to PKA-mediated phosphorylation of the fission modulator Drp1, leading to enhanced mitochondrial networks and thereby blocking apoptosis against different toxic insults. In this study, we show for the first time that AKAP121/PKA confers neuroprotection in an in vitro model of oxidative stress induced by exposure to excess glutamate. Unexpectedly, treating mouse hippocampal progenitor neuronal HT22 cells with an acute dose or chronic exposure of glutamate robustly elevates PKA signaling, a beneficial compensatory response that is phenocopied in HT22 cells conditioned to thrive in the presence of excess glutamate but not in parental HT22 cells. Secondly, redirecting the endogenous pool of PKA by transiently transfecting AKAP121 or transfecting a constitutively active mutant of PKA targeted to the mitochondrion (OMM-PKA) or of an isoform of AKAP121 that lacks the KH and Tudor domains (S-AKAP84) are sufficient to significantly block cell death induced by glutamate toxicity but not in an oxygen deprivation/reperfusion model. Conversely, transient transfection of HT22 neuronal cells with a PKA-binding-deficient mutant of AKAP121 is unable to protect against oxidative stress induced by glutamate toxicity suggesting that the catalytic activity of PKA is required for AKAP121's protective effects. Mechanistically, AKAP121 promotes neuroprotection by enhancing PKA-mediated phosphorylation of Drp1 to increase mitochondrial fusion, elevates ATP levels, and elicits an increase in the levels of antioxidants GSH and superoxide dismutase 2 leading to a reduction in the level of mitochondrial superoxide. Overall, our data supports AKAP121/PKA as a new molecular target that confers neuroprotection against glutamate toxicity by phosphorylating Drp1, to stabilize mitochondrial networks and mitochondrial function and to elicit antioxidant responses.
Keywords: A-kinase anchoring protein 121; Dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1); HT22; Mitochondrion; Oxidative stress; Protein kinase A.
Figures
References
-
- T.Coyle J, and Puttfarcken P (1993) Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262(5134), 689–695. - PubMed
-
- Gardoni F, and Di Luca M (2015) Targeting glutamatergic synapses in Parkinson’s disease. Current opinion in pharmacology 20, 24–28 - PubMed
-
- Murphy TH, Miyamoto M, Sastre A, Schnaar RL, and Coyle JT (1989) Glutamate toxicity in a neuronal cell line involves inhibition of cystine transport leading to oxidative stress. Neuron 2, 1547–1558 - PubMed
-
- Fukui M, Song JH, Choi J, Choi HJ, and Zhu BT (2009) Mechanism of glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 mouse hippocampal cells. Eur J Pharmacol 617, 1–11 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

