CaImAn an open source tool for scalable calcium imaging data analysis
- PMID: 30652683
- PMCID: PMC6342523
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.38173
CaImAn an open source tool for scalable calcium imaging data analysis
Abstract
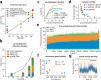
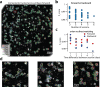
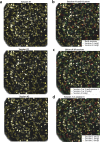
Advances in fluorescence microscopy enable monitoring larger brain areas in-vivo with finer time resolution. The resulting data rates require reproducible analysis pipelines that are reliable, fully automated, and scalable to datasets generated over the course of months. We present CaImAn, an open-source library for calcium imaging data analysis. CaImAn provides automatic and scalable methods to address problems common to pre-processing, including motion correction, neural activity identification, and registration across different sessions of data collection. It does this while requiring minimal user intervention, with good scalability on computers ranging from laptops to high-performance computing clusters. CaImAn is suitable for two-photon and one-photon imaging, and also enables real-time analysis on streaming data. To benchmark the performance of CaImAn we collected and combined a corpus of manual annotations from multiple labelers on nine mouse two-photon datasets. We demonstrate that CaImAn achieves near-human performance in detecting locations of active neurons.
Keywords: calcium imaging; data analysis; mouse; neuroscience; one-photon; open source; software; two-photon; zebrafish.
© 2019, Giovannucci et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AG, JF, PG, JK, BB, SK, JT, FN, JG, PZ, BK, DT, DC, EP No competing interests declared
Figures



References
-
- Apthorpe N, Riordan A, Aguilar R, Homann J, Gu Y, Tank D, Seung HS. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. MIT Press; 2016. Automatic Neuron Detection in Calcium Imaging Data Using Convolutional Networks; pp. 3270–3278.
-
- Berens P, Freeman J, Deneux T, Chenkov N, McColgan T, Speiser A, Macke JH, Turaga S, Mineault P, Rupprecht P, Gerhard S, Friedrich RW, Friedrich J, Paninski L, Pachitariu M, Harris KD, Bolte B, Machado TA, Ringach D, Reimer J. Community-based benchmarking improves spike inference from two-photon calcium imaging data. bioRxiv. 2017 doi: 10.1101/177956. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Botev ZI, Grotowski JF, Kroese DP. Kernel density estimation via diffusion. The Annals of Statistics. 2010;38:2916–2957. doi: 10.1214/10-AOS799. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 NS077840/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NIBIB R01EB022913/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101198/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB022913/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01NS090541/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U19 NS104648/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U19NS104648/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- F32NS077840-01/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01-MH101198/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS090541/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- FI-CCB/Simons Foundation/International
- SCGB/Simons Foundation/International
- NeuroNex DBI-1707398/National Science Foundation/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

