Population pharmacokinetics and individualized lobaplatin regimen for the treatment of Chinese small cell lung cancer in the elderly
- PMID: 30653145
- PMCID: PMC6370119
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014136
Population pharmacokinetics and individualized lobaplatin regimen for the treatment of Chinese small cell lung cancer in the elderly
Abstract
Background: Lobaplatin (LBP) is a third-generation platinum compound.
Material and methods: This prospective study was performed in 7 institutions in 2014-2016. Elderly small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients (≥65 years old) were divided into 2 groups to receive LBP regimens according to endogenous creatinine clearance rate (Ccr). LBP was administered at 30 and 20 mg/m in groups A (Ccr ≥ 80 ml/min) and B (60 ml/min ≤ Ccr < 80 ml/min), respectively. The primary endpoint was plasma LBP concentrations. Secondary endpoints were safety and efficacy parameters, including progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
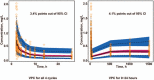
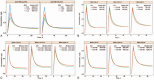
Results: One-hundred patients were enrolled. Median PFS and OS in groups A and B were 155 vs170 days and 306 vs 272 days, respectively. The rates of grade III/IV AEs in groups A and B were 60.8% (n = 31) and 51.0% (n = 25), respectively. In population pharmacokinetics, the area under the curve (AUC) value for group B was 39% lower than that of group A. With LBP administration based on body surface area (BSA), AUC differences between individuals were small.
Conclusion: With Ccr ≥ 60 ml/min, BSA based administration is necessary. Meanwhile, LBP-based regimens are reliable in treating elderly patients with SCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics and safety of lobaplatin plus etoposide in Chinese men older than 65 years with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: a phase II clinical trial.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019 Jul;84(1):73-81. doi: 10.1007/s00280-019-03828-z. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31041509 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lobaplatin (D-19466) in patients with advanced solid tumors, including patients with impaired renal of liver function.Clin Cancer Res. 1999 Sep;5(9):2349-58. Clin Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10499604 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II and pharmacokinetic study of lobaplatin in patients with relapsed ovarian cancer.Br J Cancer. 1995 Jun;71(6):1302-7. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.252. Br J Cancer. 1995. PMID: 7779728 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lobaplatin: a new antitumour platinum drug.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2001 Jan;10(1):119-28. doi: 10.1517/13543784.10.1.119. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11116285 Review.
-
Lobaplatin: D 19466.Drugs R D. 2003;4(6):369-72. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200304060-00008. Drugs R D. 2003. PMID: 14584968 Review.
References
-
- McKeage MJ. Lobaplatin: a new antitumour platinum drug. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2001;10:119–28. - PubMed
-
- Lobaplatin: D 19466. Drugs R D 2003;4:369–72. - PubMed
-
- Kou Y, Koag MC, Cheun Y, et al. Application of hypoiodite-mediated aminyl radical cyclization to synthesis of solasodine acetate. Steroids 2012;77:1069–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

