LIPG-promoted lipid storage mediates adaptation to oxidative stress in breast cancer
- PMID: 30653260
- PMCID: PMC6618071
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.32138
LIPG-promoted lipid storage mediates adaptation to oxidative stress in breast cancer
Abstract
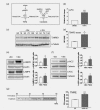
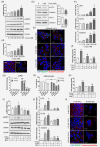
Endothelial lipase (LIPG) is a cell surface associated lipase that displays phospholipase A1 activity towards phosphatidylcholine present in high-density lipoproteins (HDL). LIPG was recently reported to be expressed in breast cancer and to support proliferation, tumourigenicity and metastasis. Here we show that severe oxidative stress leading to AMPK activation triggers LIPG upregulation, resulting in intracellular lipid droplet accumulation in breast cancer cells, which supports survival. Neutralizing oxidative stress abrogated LIPG upregulation and the concomitant lipid storage. In human breast cancer, high LIPG expression was observed in a limited subset of tumours and was significantly associated with shorter metastasis-free survival in node-negative, untreated patients. Moreover, expression of PLIN2 and TXNRD1 in these tumours indicated a link to lipid storage and oxidative stress. Altogether, our findings reveal a previously unrecognized role for LIPG in enabling oxidative stress-induced lipid droplet accumulation in tumour cells that protects against oxidative stress, and thus supports tumour progression.
Keywords: LIPG; PLIN2; TXNRD1; breast cancer; endothelial lipase; lipid droplets; oxidative stress.
© 2019 The Authors. International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Figures



Similar articles
-
FoxA and LIPG endothelial lipase control the uptake of extracellular lipids for breast cancer growth.Nat Commun. 2016 Apr 5;7:11199. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11199. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27045898 Free PMC article.
-
LIPG endothelial lipase and breast cancer risk by subtypes.Sci Rep. 2021 May 17;11(1):10436. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89669-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34001944 Free PMC article.
-
LIPG signaling promotes tumor initiation and metastasis of human basal-like triple-negative breast cancer.Elife. 2018 Jan 19;7:e31334. doi: 10.7554/eLife.31334. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29350614 Free PMC article.
-
The role of endothelial lipase in lipid metabolism, inflammation, and cancer.Histol Histopathol. 2018 Jan;33(1):1-10. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-905. Epub 2017 May 25. Histol Histopathol. 2018. PMID: 28540715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Droplets in Cancer: Guardians of Fat in a Stressful World.Molecules. 2018 Aug 3;23(8):1941. doi: 10.3390/molecules23081941. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30081476 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Perilipins in Oxidative Stress-Implications for Cardiovascular Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;13(2):209. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020209. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide expression reveals potential biomarkers in breast cancer bone metastasis.J Integr Bioinform. 2022 Apr 8;19(3):20210041. doi: 10.1515/jib-2021-0041. eCollection 2022 Sep 1. J Integr Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 35388653 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term High-Fat Diet Affected Bone Marrow Microenvironment During Aging at Single-Cell Resolution.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jul 21;6(8):e70276. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70276. eCollection 2025 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40692664 Free PMC article.
-
LIPG supports adaption to oxidative stress.EXCLI J. 2019 Jul 10;18:499-500. doi: 10.17179/excli2019-1555. eCollection 2019. EXCLI J. 2019. PMID: 31423129 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of WDR5 in breast cancer prognosis.EXCLI J. 2019 Dec 16;18:1094-1096. doi: 10.17179/excli2019-2062. eCollection 2019. EXCLI J. 2019. PMID: 31938027 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Santos CR, Schulze A. Lipid metabolism in cancer. FEBS J 2012;279:2610–23. - PubMed
-
- Kuhajda FP. Fatty acid synthase and cancer: new application of an old pathway. Cancer Res 2006;66:5977–80. - PubMed
-
- Jaye M, Lynch KJ, Krawiec J, et al. A novel endothelial‐derived lipase that modulates HDL metabolism. Nat Genet 1999;21:424–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

