Disc and nerve root findings on lumbar MRI with straightened v s flexed hips and knees-pilot study
- PMID: 30653345
- PMCID: PMC6540866
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20180851
Disc and nerve root findings on lumbar MRI with straightened v s flexed hips and knees-pilot study
Abstract
Objective:: To compare disc and nerve root findings, image quality, and pain between supine lumbar MRI positions with straightened v s flexed hips and knees.
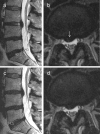
Methods:: In this prospective pilot study, 14 adults with sciatica or suspected lumbar radiculopathy underwent MRI supine with their hips and knees flexed and then straightened. For each position, two experienced radiologists assessed disc contour, location/size of disc herniation, nerve root affection, image quality, image evaluation difficulty, and sagittal angles between the vertebral bodies at each disc level L3-S1. Patients scored pain (0-10) after MRI in each position. We compared MRI assessments and mean pain scores (t-test, log-transformation) between the two positions.
Results:: We found no clear difference in disc bulges, disc herniation, nerve root affection, image quality, or image evaluation difficulty between MRI with straightened v s flexed knees/hips. Herniation size differed ≤ 0.6 mm between the two positions. Sagittal angles between neighboring vertebral bodies differed ≤3.8°. Mean pain score after MRI with straightened v s flexed knees/hips was 4.64 v s 3.29 (p = 0.005).
Conclusion:: In this pilot study, supine lumbar MRI with straightened vs flexed hips/knees showed similar disc and nerve root findings. The straightened position appeared more painful.
Advances in knowledge:: In previous studies, spondylolisthesis increased on supine MRI with straightened v s flexed lower limbs, but corresponding data on disc findings were lacking. In this pilot study, supine lumbar MRI with straightened rather than flexed hips and knees was more painful and did not improve the diagnosis of disc or nerve root findings.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anatomical evaluation of lumbar nerves using diffusion tensor imaging and implications of lateral decubitus for lateral transpsoas approach.Eur Spine J. 2017 Nov;26(11):2804-2810. doi: 10.1007/s00586-017-5082-y. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Eur Spine J. 2017. PMID: 28389885
-
Severity of foraminal lumbar stenosis and the relation to clinical symptoms and response to periradicular infiltration-introduction of the "melting sign".Spine J. 2018 Feb;18(2):294-299. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2017.07.176. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Spine J. 2018. PMID: 28739476
-
Successful visualization of dynamic change of lumbar nerve root compression with the patient in both upright and prone positions using dynamic digital tomosynthesis-radiculography in patients with lumbar foraminal stenosis: An initial report of three cases.J Clin Neurosci. 2019 Apr;62:256-259. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2018.12.016. Epub 2019 Jan 9. J Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30638782
-
Use of MRI in diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy: case report and review of the literature.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2018 Nov;160(11):2225-2227. doi: 10.1007/s00701-018-3664-z. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2018. PMID: 30203363 Review.
-
Relationships between paraspinal muscle morphology and neurocompressive conditions of the lumbar spine: a systematic review with meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018 Sep 27;19(1):351. doi: 10.1186/s12891-018-2266-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018. PMID: 30261870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tarantino U , Fanucci E , Iundusi R , Celi M , Altobelli S , Gasbarra E , et al. . Lumbar spine MRI in upright position for diagnosing acute and chronic low back pain: statistical analysis of morphological changes . J Orthopaed Traumatol 2013. ; 14 : 15 – 22 . doi: 10.1007/s10195-012-0213-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

