Red blood cell alloimmunisation in transfusion-dependent thalassaemia: a systematic review
- PMID: 30653458
- PMCID: PMC6343597
- DOI: 10.2450/2019.0229-18
Red blood cell alloimmunisation in transfusion-dependent thalassaemia: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Chronic red blood cell transfusion is the first-line treatment for severe forms of thalassaemia. This therapy is, however, hampered by a number of adverse effects, including red blood cell alloimmunisation. The aim of this systematic review was to collect the current literature data on erythrocyte alloimmunisation.
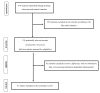
Materials and methods: We performed a systematic search of the literature which identified 41 cohort studies involving 9,256 patients.
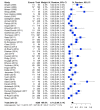
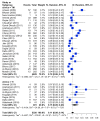
Results: The prevalence of erythrocyte alloimmunisation was 11.4% (95% CI: 9.3-13.9%) with a higher rate of alloimmunisation against antigens of the Rh (52.4%) and Kell (25.6%) systems. Overall, alloantibodies against antigens belonging to the Rh and Kell systems accounted for 78% of the cases. A higher prevalence of red blood cell alloimmunisation was found in patients with thalassaemia intermedia compared to that among patients with thalassaemia major (15.5 vs 12.8%).
Discussion: Matching transfusion-dependent thalassaemia patients and red blood cell units for Rh and Kell antigens should be able to reduce the risk of red blood cell alloimmunisation by about 80%.
Conflict of interest statement
Giancarlo M. Liumbruno is the Editor-in-Chief of Blood Transfusion. As a result, this manuscript was subjected to an additional external review. The Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Compernolle V, Chou ST, Tanael S, et al. for the International Collaboration for Transfusion Medicine Guidelines. Red blood cell specifications for patients with hemoglobinopathies: a systematic review and guideline. Transfusion. 2018;58:1555–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
