Molecular typing of Streptococcus suis strains isolated from diseased and healthy pigs between 1996-2016
- PMID: 30653570
- PMCID: PMC6336254
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210801
Molecular typing of Streptococcus suis strains isolated from diseased and healthy pigs between 1996-2016
Abstract
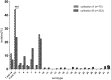
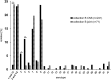
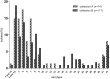
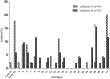
Streptococcus suis is an economically important pathogen of pigs as well as a zoonotic cause of human disease. Serotyping is used for further characterization of isolates; some serotypes seem to be more virulent and more widely spread than others. This study characterizes a collection of German field isolates of Streptococcus suis from pigs dating from 1996 to 2016 with respect to capsular genes (cps) specific for individual serotypes and pathotype by multiplex PCR and relates results to the clinical background of these isolates. The most prominent finding was the reduction in prevalence of serotype-2/serotype-1/2 among invasive isolates during this sampling period, which might be attributed to widely implemented autogenous vaccination programs in swine against serotype 2 in Germany. In diseased pigs (systemically ill; respiratory disease) isolates of serotype-1/serotype-14, serotype-2/serotype-1/2, serotype 3 to 5 and 7 to 9 were most frequent while in carrier isolates a greater variety of cps types was found. Serotype-1/serotype-14 seemed to be preferentially located in joints, serotype 4 and serotype 3 in the central nervous system, respectively. The virulence associated extracellular protein factor was almost exclusively associated with invasive serotype-1/serotype-14 and serotype-2/serotype-1/2 isolates. In contrast, lung isolates of serotype-2/serotype-1/2 mainly harbored the gene for muramidase-released protein. Serotype 4 and serotype 9 isolates from clinically diseased pigs most frequently carried the muramidase-released protein gene and the suilysin gene. When examined by transmission electron microscopy all but one of the isolates which were non-typable by molecular and serological methods showed various amounts of capsular material indicating potentially new serotypes among these isolates. Given the variety of cps types/serotypes detected in pigs, not only veterinarians but also medical doctors should consider other serotypes than just serotype 2 when investigating potential human cases of Streptococcus suis infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Staats JJ, Feder I, Okwumabua O, Chengappa MM. Streptococcus suis: past and present. Vet Res Commun. 1997;21(6):381–407. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

