Sildenafil does not improve performance in 16.1 km cycle exercise time-trial in acute hypoxia
- PMID: 30653578
- PMCID: PMC6336365
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210841
Sildenafil does not improve performance in 16.1 km cycle exercise time-trial in acute hypoxia
Abstract
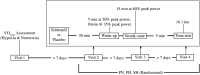
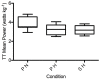
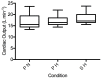
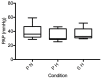
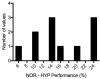
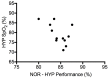
Sildenafil is a pulmonary vasodilator that has potential to mitigate the decrement in endurance performance caused by hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of sildenafil on pulmonary artery pressure, cardiac output, pulse oxygen saturation, and exercise performance at moderate simulated altitude. We hypothesized that sildenafil would reduce the decline in exercise performance in hypoxia by blunting the rise in pulmonary artery pressure and causing a relative increase in cardiac output and oxygen saturation. Twelve endurance trained men performed three experimental cycling trials at sea level and simulated moderate altitude of 3,000m (FIO2 = 0.147) after ingesting either a placebo or sildenafil 50 mg capsule in a double blinded fashion. Each test consisted of a warmup period, a 15-minute steady state period at 60% of peak power output, and a 16.1 km time-trial. All subjects experienced a decline in maximal exercise capacity in hypoxia that ranged from 6% to 24%. This decline was correlated with the reduction in pulse oxygen saturation in hypoxic maximal exercise. Sildenafil had no effect on pulmonary artery pressure, cardiac output, or pulse oxygen saturation measured during steady state exercise. There was no effect of sildenafil on mean power output during the time-trial. During high intensity cycle exercise in acute, moderate hypoxia pulmonary artery pressure is unaffected by sildenafil and does not appear to influence cardiovascular function or exercise performance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Jensen KS, Micco AJ, Czartolomna J, Latham L, Voelkel NF. Rapid onset of hypoxic vasoconstriction in isolated lungs. JAP. 1992;72(5):2018–23. - PubMed
-
- Wagner PD, Gale GE, Moon RE, Torre-Bueno JR, Stolp BW, Saltzman HA. Pulmonary gas exchange in humans exercising at sea level and simulated altitude. JAP. 1986;61(1):260–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

