Induction of phytoalexins and proteins related to pathogenesis in plants treated with extracts of cutaneous secretions of southern Amazonian Bufonidae amphibians
- PMID: 30653617
- PMCID: PMC6336429
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211020
Induction of phytoalexins and proteins related to pathogenesis in plants treated with extracts of cutaneous secretions of southern Amazonian Bufonidae amphibians
Abstract
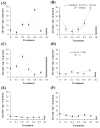
Cutaneous secretions produced by amphibians of the family Bufonidae are rich sources of bioactive compounds that can be useful as new chemical templates for agrochemicals. In crop protection, the use of elicitors to induce responses offers the prospect of durable, broad-spectrum disease control using the plant's own resistance. Therefore, we evaluated the potential of methanolic extracts of cutaneous secretions of two species of amphibians of the family Bufonidae found in the Amazon biome-Rhaebo guttatus (species 1) and Rhinella marina (species 2)-in the synthesis of phytoalexins in soybean cotyledons, bean hypocotyls, and sorghum mesocotyls. Additionally, changes in the enzyme activity of β-1,3-glucanase, peroxidase (POX), and polyphenol oxidase (PPO) and in the total protein content of soybean cotyledons were determined. In the soybean cultivar 'TMG 132 RR', our results indicated that the methanolic extract of R. guttatus cutaneous secretions suppressed glyceollin synthesis and β-1,3-glucanase activity and increased POX and PPO activities at higher concentrations and total protein content at a concentration of 0.2 mg/mL. On the other hand, the methanolic extract of R. marina cutaneous secretions induced glyceollin synthesis in the soybean cultivars 'TMG 132 RR' and 'Monsoy 8372 IPRO' at 0.1-0.2 mg/mL and 0.2 mg/mL, respectively. The methanolic extract of R. marina cutaneous secretions also increased the specific activity of POX and PPO in 'Monsoy 8372 IPRO' and 'TMG 132 RR', respectively, and decreased the activity of β-1,3-glucanases in 'Monsoy 8372 IPRO'. At 0.3 mg/mL, it stimulated phaseolin synthesis. The extracts did not express bioactivity in the synthesis of deoxyanthocyanidins in sorghum mesocotyls. The study in soybean suggests that the bioactivity in defense responses is influenced by cultivar genotypes. Therefore, these results provide evidence that extracts of cutaneous secretions of these amphibians species may contribute to the bioactivity of defense metabolites in plants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Antiproliferative activity of Rhinella marina and Rhaebo guttatus venom extracts from Southern Amazon.Toxicon. 2013 Sep;72:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.06.009. Epub 2013 Jun 22. Toxicon. 2013. PMID: 23796725
-
Larvicidal activity of the skin secretion ofRhinella marina and Rhaebo guttatus (Anura: Bufonidae) against the Brazilian malaria vector, Anopheles darlingi (Diptera: Culicidae).Trop Biomed. 2021 Dec 1;38(4):505-510. doi: 10.47665/tb.38.4.096. Trop Biomed. 2021. PMID: 35001918
-
Comparative study of the chemical profile of the parotoid gland secretions from Rhaebo guttatus from different regions of the Brazilian Amazon.Toxicon. 2020 May;179:101-106. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2020.03.005. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Toxicon. 2020. PMID: 32209334
-
Glyceollin, a soybean phytoalexin with medicinal properties.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Apr;90(1):59-68. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3169-7. Epub 2011 Feb 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21336922 Review.
-
Antimicrobial Secretions of Toads (Anura, Bufonidae): Bioactive Extracts and Isolated Compounds against Human Pathogens.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Nov 26;9(12):843. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9120843. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33255881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomics Insights into Chemical Convergence in Xanthomonas perforans and Metabolic Changes Following Treatment with the Small Molecule Carvacrol.Metabolites. 2021 Dec 16;11(12):879. doi: 10.3390/metabo11120879. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34940636 Free PMC article.
-
Eruca sativa seed napin structural insights and thorough functional characterization.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 15;11(1):24066. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02174-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34911985 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic changes in green bean pods against grey mould and white rot diseases via field application of chemical elicitor nanoparticles.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020 Sep;14(7):574-583. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2020.0004. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33010132 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Salicylic Acid and Indole Acetic Acid Exogenous Applications on Induction of Faba Bean Resistance against Orobanche crenata.Plant Pathol J. 2020 Oct 1;36(5):476-490. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.03.2020.0056. Plant Pathol J. 2020. PMID: 33082732 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of salicylic acid, benzothiadiazole, and other commercial biostimulants on boosting faba bean (Vicia faba L.) tolerance against Orobanche spp.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 9;20(6):e0324976. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324976. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40489516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cabral LC, Pinto VF, Patriarca A. Application of plant derived compounds to control fungal spoilage and mycotoxin production in foods. Int J Food Microbiol. 2013;166: 1–14. - PubMed
-
- Singh R, Chandrawat KS. Role of phytoalexins in plant disease resistance. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2017;6: 125–129.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

