No effect of beetroot juice supplementation on exercise economy and performance in recreationally active females despite increased torque production
- PMID: 30653856
- PMCID: PMC6336290
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13982
No effect of beetroot juice supplementation on exercise economy and performance in recreationally active females despite increased torque production
Abstract
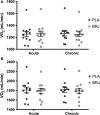
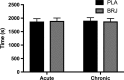
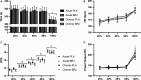
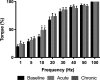
This study investigated the effects of acute and chronic beetroot juice (BRJ) supplementation on submaximal exercise oxygen uptake (VO2 ), time trial (TT) performance, and contractile properties of the plantar flexors in females. Study 1: Using a double blind, randomized, crossover design, 12 recreationally active females using hormonal contraceptives supplemented acutely (2.5 h) and chronically (8 days) with 280 mL BRJ/d (~26 mmoles nitrate [ ]) or a -free placebo (PLA). On days 1 and 8, participants cycled for 10 min at 50% and 70% VO2peak and completed a 4 kJ/kg body mass TT. Plasma [ ] and nitrite ([NO2- ]) increased significantly following BRJ supplementation versus PLA. There was no effect of BRJ supplementation on VO2 at 50% or 70% VO2peak , or TT performance. Study 2: 12 recreationally active females (n = 7 from Study 1) using hormonal contraceptives participated in a baseline visit and were supplemented acutely (2.5 h) and chronically (8 days) with 280 mL BRJ/d. Maximum voluntary strength (MVC) of the plantar flexors was assessed and a torque-frequency curve performed. BRJ had no effect on MVC, voluntary activation, peak twitch torque, time to peak torque, or half relaxation time. Following both acute (46.6 ± 4.9% of 100 Hz torque) and chronic (47.2 ± 4.4%) supplementation, 10 Hz torque was significantly greater compared to baseline (32.9 ± 2.6%). In summary, BRJ may not be an effective ergogenic aid in recreationally active females as it did not reduce submaximal exercise VO2 or improve aerobic TT performance despite increasing low frequency torque production.
Keywords: Beetroot juice; contractile properties; females; oxygen uptake; performance; torque-frequency.
© 2019 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Beetroot juice supplementation reduces whole body oxygen consumption but does not improve indices of mitochondrial efficiency in human skeletal muscle.J Physiol. 2016 Jan 15;594(2):421-35. doi: 10.1113/JP270844. Epub 2015 Dec 16. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26457670 Free PMC article.
-
No Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on 100-m and 200-m Swimming Performance in Moderately Trained Swimmers.Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019 Jul 1;14(6):706-710. doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2018-0654. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019. PMID: 30427246 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Oral Supplementation With Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice in Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension-Results From BEET-PAH, an Exploratory Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study.J Card Fail. 2018 Oct;24(10):640-653. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Sep 20. J Card Fail. 2018. PMID: 30244181 Clinical Trial.
-
The benefits and risks of beetroot juice consumption: a systematic review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(5):788-804. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1746629. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32292042
-
Influence of dietary nitrate on the physiological determinants of exercise performance: a critical review.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014 Sep;39(9):1019-28. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2014-0036. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014. PMID: 25068792 Review.
Cited by
-
Beetroot as a functional food with huge health benefits: Antioxidant, antitumor, physical function, and chronic metabolomics activity.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Sep 9;9(11):6406-6420. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2577. eCollection 2021 Nov. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34760270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Back Squat and Bench Press Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2023 May 27;15(11):2493. doi: 10.3390/nu15112493. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37299456 Free PMC article.
-
Beetroot juice ingestion does not improve neuromuscular performance and match-play demands in elite female hockey players: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.Eur J Nutr. 2023 Apr;62(3):1123-1130. doi: 10.1007/s00394-022-03052-1. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Eur J Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36401662 Clinical Trial.
-
Ergogenic Aids to Improve Physical Performance in Female Athletes: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 24;15(1):81. doi: 10.3390/nu15010081. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36615738 Free PMC article.
-
Active Women Across the Lifespan: Nutritional Ingredients to Support Health and Wellness.Sports Med. 2022 Dec;52(Suppl 1):101-117. doi: 10.1007/s40279-022-01755-3. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 36173598 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bailey, S. J. , Winyard P., Vanhatalo A., Blackwell J. R., DiMenna F. J., Wilkerson D. P., et al. 2009. Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of low‐intensity exercise and enhances tolerance to high‐intensity exercise in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 107:1144–1155. 10.1152/japplphysiol.00722.2009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bailey, S. J. , Vanhatalo A., Winyard P. G., and Jones A. M.. 2012. The nitrate‐nitrite‐nitric oxide pathway: its role in human exercise physiology. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 12:309–320. 10.1080/17461391.2011.635705. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

