Drug Bioavailability Enhancing Agents of Natural Origin (Bioenhancers) that Modulate Drug Membrane Permeation and Pre-Systemic Metabolism
- PMID: 30654429
- PMCID: PMC6359194
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11010033
Drug Bioavailability Enhancing Agents of Natural Origin (Bioenhancers) that Modulate Drug Membrane Permeation and Pre-Systemic Metabolism
Abstract
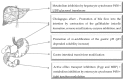
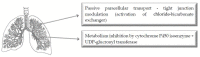
Many new chemical entities are discovered with high therapeutic potential, however, many of these compounds exhibit unfavorable pharmacokinetic properties due to poor solubility and/or poor membrane permeation characteristics. The latter is mainly due to the lipid-like barrier imposed by epithelial mucosal layers, which have to be crossed by drug molecules in order to exert a therapeutic effect. Another barrier is the pre-systemic metabolic degradation of drug molecules, mainly by cytochrome P450 enzymes located in the intestinal enterocytes and liver hepatocytes. Although the nasal, buccal and pulmonary routes of administration avoid the first-pass effect, they are still dependent on absorption of drug molecules across the mucosal surfaces to achieve systemic drug delivery. Bioenhancers (drug absorption enhancers of natural origin) have been identified that can increase the quantity of unchanged drug that appears in the systemic blood circulation by means of modulating membrane permeation and/or pre-systemic metabolism. The aim of this paper is to provide an overview of natural bioenhancers and their main mechanisms of action for the nasal, buccal, pulmonary and oral routes of drug administration. Poorly bioavailable drugs such as large, hydrophilic therapeutics are often administered by injections. Bioenhancers may potentially be used to benefit patients by making systemic delivery of these poorly bioavailable drugs possible via alternative routes of administration (i.e., oral, nasal, buccal or pulmonary routes of administration) and may also reduce dosages of small molecular drugs and thereby reduce treatment costs.
Keywords: P-glycoprotein; bioenhancer; cytochrome P450; drug absorption enhancer; efflux; metabolism; pharmacokinetic interaction; tight junction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plant based Bioavailability Enhancers.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(8):642-654. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220112141355. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 35023453 Review.
-
Role of herbal bioactives as a potential bioavailability enhancer for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients.Fitoterapia. 2014 Sep;97:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2014.05.005. Epub 2014 May 23. Fitoterapia. 2014. PMID: 24862064 Review.
-
Evaluation of Drug Permeation Enhancement by Using In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 31;18(2):195. doi: 10.3390/ph18020195. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical evaluation of permeation enhancers for oral mucosal drug delivery.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2010 Mar;36(3):254-82. doi: 10.1080/03639040903117348. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2010. PMID: 19663558 Review.
-
Myriad Molecules to Overcome Efflux Drug Transporters and Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes: A Journey from Synthetic to Natural.Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2015;32(5):441-60. doi: 10.1615/critrevtherdrugcarriersyst.2015012019. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2015. PMID: 26559434 Review.
Cited by
-
Modification of Peptide and Permeation Enhancer In Vitro Release Rates by Dispersion with a Gel-Forming Polymer.Pharm Res. 2025 Jun;42(6):1003-1020. doi: 10.1007/s11095-025-03870-y. Epub 2025 Jun 6. Pharm Res. 2025. PMID: 40481297 Free PMC article.
-
Function of Green Tea Catechins in the Brain: Epigallocatechin Gallate and its Metabolites.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 25;20(15):3630. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153630. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31349535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Epithelial Barrier Integrity Enhancers-Citrus medica and Origanum dayi Extracts.Gels. 2024 Dec 19;10(12):836. doi: 10.3390/gels10120836. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39727593 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the potential of Glycyrrhiza glabra as a bioavailability enhancer of Vitamin B12.Front Nutr. 2022 Oct 28;9:1038902. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1038902. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36386946 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Polydatin Against Dementia-Related Disorders.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(2):127-135. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200611144825. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32525774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Navia M.A., Chaturvedi P.R. Design principles for orally bioavailable drugs. Drug Discov. Today. 1996;1:179–189. doi: 10.1016/1359-6446(96)10020-9. - DOI
-
- Chillistone S., Hardman J. Factors affecting drug absorption and distribution. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2008;9:167–171. doi: 10.1016/j.mpaic.2008.02.005. - DOI
-
- Sikic B.I. Modulation of multidrug resistance: A paradigm for translational clinical research. Oncology. 1999;13:183–187. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

