Dual Role of Triptolide in Interrupting the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway to Attenuate Cardiac Fibrosis
- PMID: 30654511
- PMCID: PMC6359320
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20020360
Dual Role of Triptolide in Interrupting the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway to Attenuate Cardiac Fibrosis
Abstract
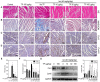
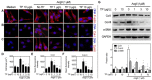
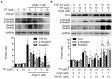
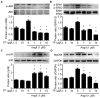
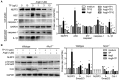
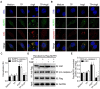
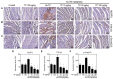
In a previous paper, we reported that triptolide (TP), a commonly used immunomodulator, could attenuate cardiac hypertrophy. This present study aimed to further explore the inhibition of cardiac fibrosis by TP and the possible mechanism from the perspective of the NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. Hematoxylin-eosin and Masson's staining, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence were performed to observe cardiac fibrotic changes in mice and mouse cardiac fibroblasts (CFs). The Western blot, colocalization, and immunoprecipitation were applied to detect protein expression and interactions. Results suggested that TP dose-dependently inhibited cardiac fibrosis induced by isoproterenol and collagen production of CFs induced by angiotensin II. TP exhibited an antifibrotic effect via inhibiting activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, which sequentially decreased IL-1β maturation, myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88)-related phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), extracellular regulated protein kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), and TGF-β1/Smad signaling, and ultimately resulted in less collagen production. Moreover, TP showed no antifibrotic effect in Nlrp3-knockout CFs. Notably, TP inhibited the expression of NLRP3 and apoptosis-associated speck-like proteins containing a caspase recruitment domain (ASC) as well as inflammasome assembly, by interrupting the NLRP3-ASC interaction to inhibit inflammasome activation. Finally, TP indeed inhibited the NLRP3-TGFβ1-Smad pathway in vivo. Conclusively, TP was found to play a dual role in interrupting the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome to attenuate cardiac fibrosis.
Keywords: NOD-like receptor protein 3; apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; cardiac fibrosis; inflammasome; triptolide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Triptolide inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and ameliorates podocyte epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by high glucose].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Dec;44(24):5457-5464. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20191114.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 32237395 Chinese.
-
Triptolide attenuates pressure overload-induced myocardial remodeling in mice via the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome expression.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Mar 25;485(1):69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.021. Epub 2017 Feb 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28202417
-
Serelaxin inhibits the profibrotic TGF-β1/IL-1β axis by targeting TLR-4 and the NLRP3 inflammasome in cardiac myofibroblasts.FASEB J. 2019 Dec;33(12):14717-14733. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901079RR. Epub 2019 Nov 5. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31689135
-
Negative regulators and their mechanisms in NLRP3 inflammasome activation and signaling.Immunol Cell Biol. 2017 Aug;95(7):584-592. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.23. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28356568 Review.
-
Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome by Phosphorylation.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 8;9:2305. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02305. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30349539 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Impact of Bioactive Compounds as NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitors: An Update.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(13):1719-1746. doi: 10.2174/0113892010276859231125165251. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38173061 Review.
-
The role of pyroptosis in heart failure and related traditional chinese medicine treatments.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 28;15:1377359. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1377359. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38868667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diterpenes: Nature's Hidden Gems of Immunomodulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 3;26(5):2250. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052250. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting pyroptosis in myocardial inflammation and fibrosis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Apoptosis. 2025 Jul 23. doi: 10.1007/s10495-025-02151-8. Online ahead of print. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 40702245 Review.
-
Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain-Like Receptor 3 Deficiency Attenuated Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis via Reactive Oxygen Species/High Mobility Group Box 1 Protein Axis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 11;8:713. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00713. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32850832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C., Yang S., Zhang M., Zhang Z., Hong J., Han D., Ma J., Zhang S.B., Okunieff P., Zhang L. Triptolide mitigates radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis via inhibition of axis of alveolar macrophages-NOXes-ROS-myofibroblasts. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016;17:381–389. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1139229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

